The Second Animal on Earth: Unraveling the Early Evolution of Life
The history of life on Earth is a fascinating subject that has intrigued scientists and enthusiasts alike for centuries. As we explore the origins of life, one question arises: What was the second animal on Earth? In this article, we will delve into the early stages of evolution and shed light on the identity of the second animal to emerge on our planet.
1. The Origins of Life:
To understand the second animal on Earth, it is crucial to explore the origins of life itself. The Earth formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago, and evidence suggests that life emerged relatively early in our planet's history. The first forms of life were simple, single-celled organisms that inhabited the oceans.
2. The First Animal:
The first animal on Earth was likely a sponge, belonging to the phylum Porifera. Sponges are multicellular organisms characterized by their ability to filter water and extract nutrients. These early animals appeared around 640 million years ago during the Ediacaran period and played a significant role in shaping the subsequent evolution of life.
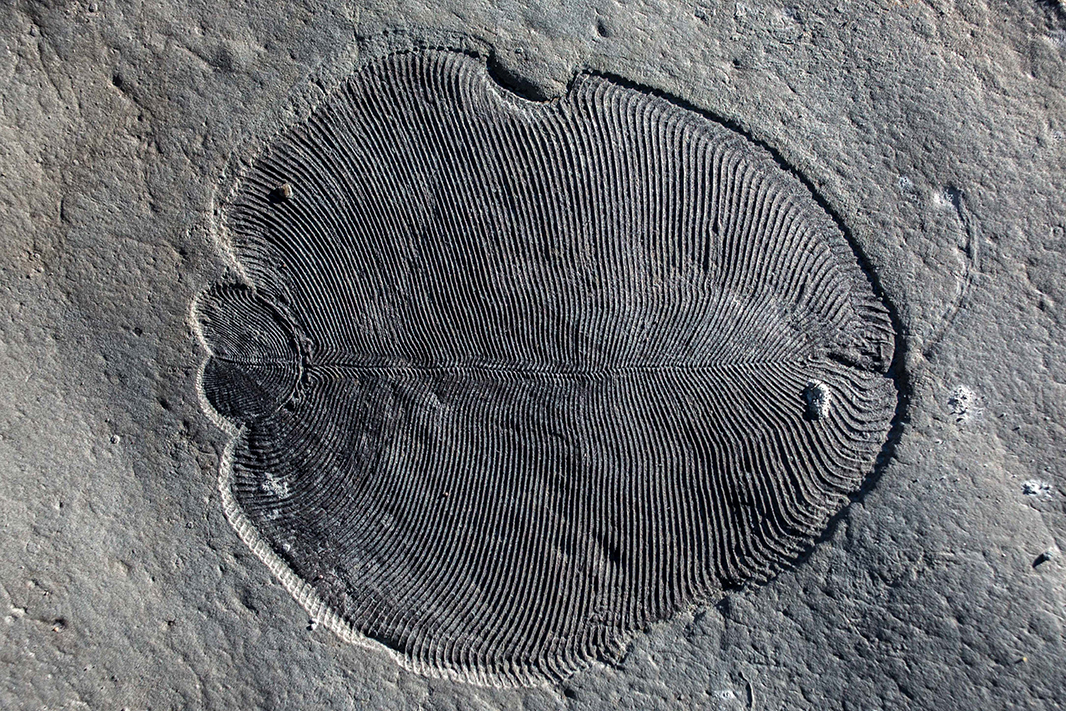

First Animal
3. The Second Animal:
Determining the identity of the second animal on Earth is a challenging task due to the limited fossil record and the complexity of evolutionary history. However, based on current scientific understanding, it is believed that the second animal to emerge after sponges was a comb jelly, scientifically known as ctenophores.
4. Comb Jellies:
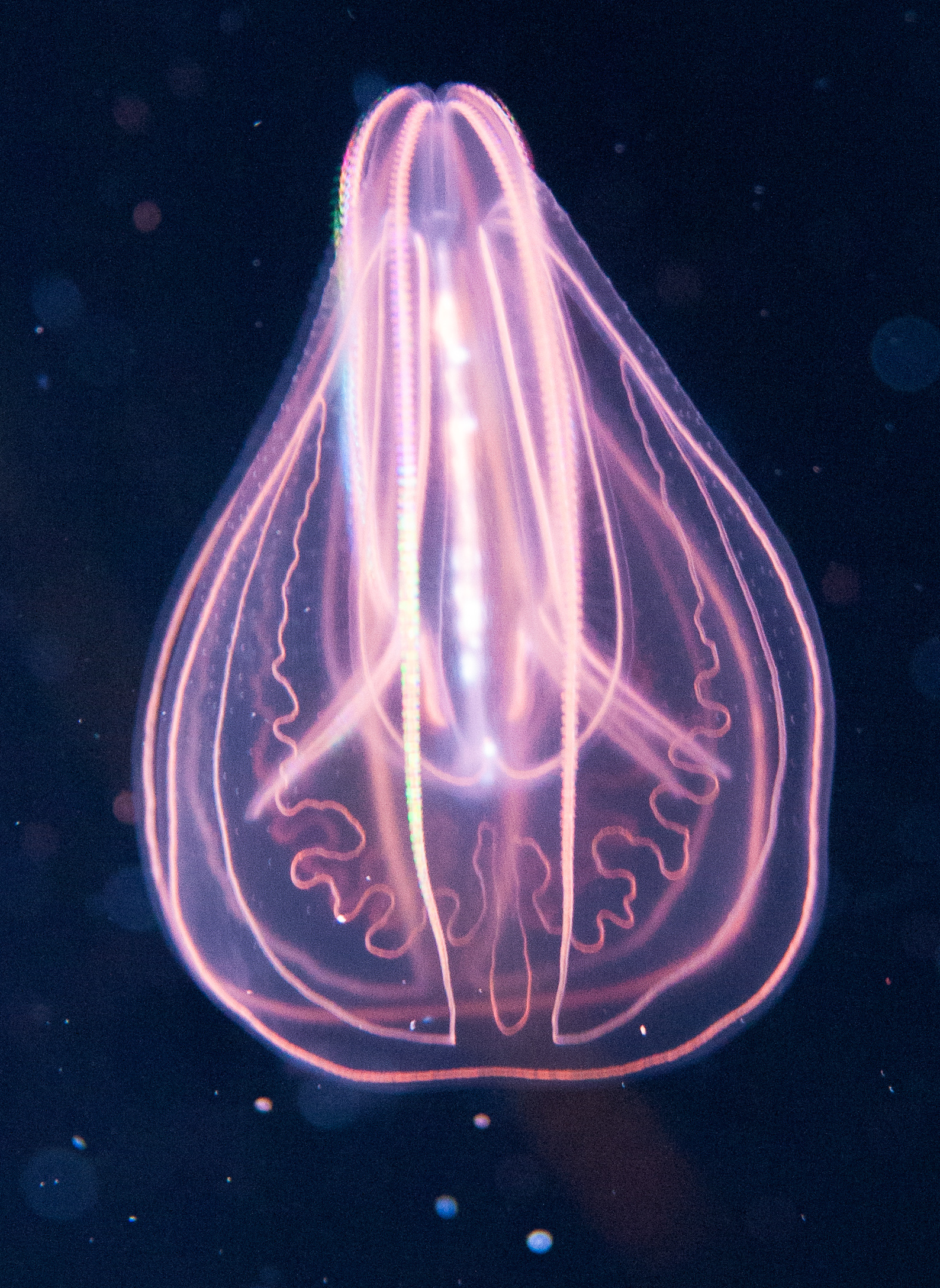
Comb Jellies
Ctenophores, commonly referred to as comb jellies, are gelatinous marine animals found in oceans worldwide. They possess a distinctive feature called "combs," rows of cilia that create mesmerizing light displays as they move through the water. Comb jellies have a simple body structure and are known for their bioluminescence.
5. Fossil Evidence and Phylogenetic Analysis:
Determining the second animal on Earth relies on both fossil evidence and phylogenetic analysis. Fossils of comb jellies are extremely rare due to their delicate nature, making it difficult to establish a precise timeline. However, recent studies using genomic data and molecular analysis have provided insights into the evolutionary relationships among early animal groups.
6. The Significance of Comb Jellies:
Understanding the emergence of comb jellies is crucial to unraveling the early evolution of animals. These organisms represent an important branch in the tree of life and offer valuable insights into the development of complex animal traits and ecological interactions. Their unique characteristics and evolutionary history contribute to our understanding of the diversification of life on Earth.
7. The Complexity of Early Animal Evolution:
The evolution of animals during the early stages of life on Earth was a complex and dynamic process. It involved the development of various body plans, adaptations to different environments, and the emergence of specialized features. Studying the second animal and subsequent evolutionary milestones provides a glimpse into the remarkable diversity and adaptability of life forms.
8. Further Research and Discoveries:
Scientific research into the origins and early evolution of animals is ongoing. New discoveries, advanced techniques, and interdisciplinary collaborations continue to shed light on the mysteries of the past. As our knowledge expands, we may uncover additional insights into the identity of the second animal on Earth and gain a deeper understanding of the intricate web of life.
While the exact identity of the second animal on Earth may remain somewhat elusive, current scientific evidence points to comb jellies, or ctenophores, as strong candidates. The emergence of these gelatinous marine organisms after the initial appearance of sponges marks an important milestone in the evolutionary history of animals. As scientific exploration and technological advancements progress, we can anticipate further discoveries and a more comprehensive understanding of the early stages of life's journey on our planet.