What Temperature Melts Lead: Exploring the Melting Point of Lead
Lead is a widely known metal with various applications in industries ranging from construction to electronics. Understanding the melting point of lead is crucial for safety measures, industrial processes, and scientific research. In this article, we will delve into the topic and provide comprehensive information about the temperature at which lead melts.
1. What is Lead?

What is Lead
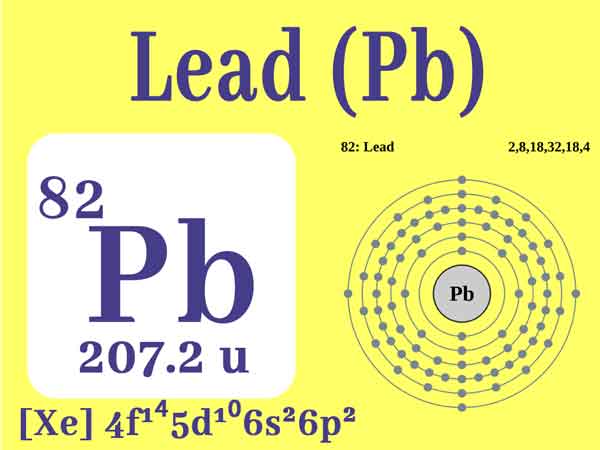
Lead is a heavy metal with the atomic number 82 and symbol Pb (derived from the Latin word "plumbum"). It has been used by humans for thousands of years due to its malleability, low melting point, and resistance to corrosion. Its applications include batteries, soldering, construction materials, and radiation shielding.
2. Properties of Lead:
Properties of Lead
Lead possesses several notable properties that make it useful in various industries. It is a soft and dense metal, with a bluish-white appearance when freshly cut. Additionally, lead is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for long-term use in different environments.
3. The Melting Point of Lead:
The melting point of lead is a fundamental characteristic that determines its behavior under different conditions. At this temperature, lead transforms from a solid state to a liquid state. The melting point of lead is affected by factors such as impurities and pressure variations.
4. Determining the Melting Point:
The melting point of lead is commonly determined using various methods, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and direct observation. DSC measures the heat flow associated with the phase transition, providing accurate results. Direct observation involves visually inspecting the sample while gradually increasing the temperature until melting occurs.
5. Melting Point of Lead:
Lead has a relatively low melting point compared to other metals. The accepted melting point of lead is approximately 327.5 degrees Celsius or 621.5 degrees Fahrenheit. However, it's important to note that impurities present in lead alloys can slightly alter this temperature.
6. Comparison with Other Metals:
To better understand the significance of the lead's melting point, let's compare it with the melting points of other common metals:
- Copper: Melting point at around 1,085 degrees Celsius or 1,985 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Aluminum: Melting point at approximately 660 degrees Celsius or 1,220 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Iron: Melting point at about 1,535 degrees Celsius or 2,795 degrees Fahrenheit.
7. Factors Affecting the Melting Point:
Several factors can influence the melting point of lead, including impurities, pressure, and the presence of other elements in alloys. Impurities can lower or raise the melting point, while increased pressure can slightly increase the melting point.
8. Applications of the Melting Point of Lead:
Understanding the melting point of lead is crucial in various industries. For example:
- Soldering: Lead-based solder is widely used in electronic circuits, and knowing the melting point ensures proper application.
- Safety Measures: Understanding the melting point helps prevent lead exposure during industrial processes or lead-related accidents.
- Scientific Research: Researchers studying lead-based materials and their properties rely on accurate melting point information.
The melting point of lead plays a vital role in numerous industries and scientific research. With a melting point of approximately 327.5 degrees Celsius or 621.5 degrees Fahrenheit, lead's behavior can be controlled and utilized effectively. By comprehending this fundamental characteristic, professionals can make informed decisions regarding lead-based materials, safety measures, and industrial processes.