What Part of the Body Has the Most Nerve Endings?
The human body is a complex and fascinating system, comprising various organs, tissues, and cells. Nerve endings play a crucial role in our sensory perception, enabling us to experience touch, pain, and temperature. In this article, we will explore the question, "What part of the body has the most nerve endings?" and delve into the regions that are particularly rich in these sensory receptors.
1. Skin
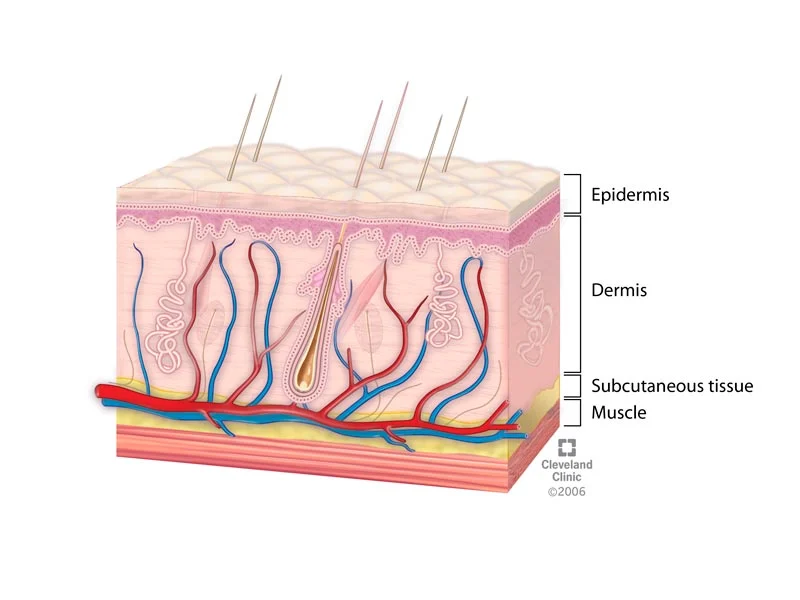
Skin
The skin is the largest organ of the human body and serves as a protective barrier between the internal organs and the external environment. It is also home to a vast network of nerve endings. The skin contains numerous sensory receptors, such as Merkel cells, Meissner's corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles, and Ruffini endings, which allow us to detect various sensations, including pressure, temperature, and pain.
2. Fingertips

Fingertips
When it comes to sensitivity and touch, our fingertips are highly specialized. They are densely populated with nerve endings, making them one of the most sensitive parts of our body. This heightened sensitivity in our fingertips allows us to perceive fine textures and discriminate between objects with precision.
3. Lips
The lips are not only essential for speech and eating but also for experiencing sensations. Similar to our fingertips, the lips contain a high concentration of nerve endings. This abundance of sensory receptors enables us to detect subtle changes in temperature, pressure, and texture, allowing for a heightened sensory experience during activities such as kissing or tasting food.
4. Genital Area
The genital area, particularly in males, has a significant concentration of nerve endings. The penile foreskin, clitoris, and vaginal walls are rich in sensory receptors, contributing to sexual pleasure and sensitivity. These nerve endings play a vital role in sexual arousal and orgasm.
5. Tongue
The tongue is crucial for our sense of taste, but it also possesses a large number of nerve endings. Taste buds located on the surface of the tongue allow us to discern different flavors, while the nerve endings facilitate the transmission of taste signals to the brain. The tongue's sensitivity helps us enjoy the diverse range of tastes that food and beverages offer.
6. Cornea
The cornea, the transparent outer layer of the eye, is densely populated with nerve endings. These nerve endings are responsible for our ability to perceive sensations such as touch and pain in the eye. They play a crucial role in triggering the blink reflex and protecting the eye from potential damage.
7. Ears
While the ears are primarily associated with hearing, they also house nerve endings responsible for our sense of balance and spatial orientation. The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, contains specialized nerve endings that detect motion and provide information about our head position and movement.
The human body is a remarkable creation with various parts rich in nerve endings. From the skin to the fingertips, lips, genital area, tongue, cornea, and ears, these regions house an abundance of sensory receptors that allow us to experience touch, taste, pain, and other sensations. Understanding the distribution of nerve endings in our body helps us appreciate the complexity and intricacy of our sensory perception.