How Bad is My Batch: A Comprehensive Guide to Evaluating Product Quality
In the world of manufacturing and production, the quality of a batch can have a profound impact on a company's success. Identifying and addressing batch quality issues is crucial to maintaining customer satisfaction and the integrity of your brand. In this guide, we'll explore the concept of batch quality and provide insights into how to assess and improve it effectively.
1. Understanding Batch Quality:

Batch Quality
Before we delve into evaluating batch quality, let's define what it means. Batch quality refers to the overall standard and consistency of products produced within a specific batch or production run. It encompasses various factors, including product specifications, defects, and adherence to quality standards.
2. Set Clear Quality Standards:
To determine how bad your batch is, you must have clear quality standards in place. These standards should outline the desired attributes and specifications of the products within a batch. Without well-defined standards, it becomes challenging to assess batch quality accurately.
3. Regular Inspection and Testing:
Regular inspection and testing are essential components of evaluating batch quality. Implement quality control processes that involve thorough inspections and testing at various stages of production. This helps identify issues early in the process, reducing the likelihood of producing a bad batch.
4. Statistical Process Control (SPC):
Utilize statistical process control techniques to monitor and analyze batch quality data. SPC allows you to identify trends, variations, and anomalies in the production process, helping you pinpoint areas that need improvement.
5. Root Cause Analysis:
When you encounter a bad batch, it's crucial to conduct a root cause analysis. Determine the underlying factors that led to the batch's poor quality. This analysis can reveal systemic issues that require corrective action.
6. Supplier Evaluation:
Evaluate the quality of raw materials and components supplied by your vendors. Poor-quality inputs can significantly impact batch quality. Maintain strong relationships with suppliers who consistently provide high-quality materials.
7. Employee Training and Engagement:
Invest in employee training and engagement to ensure they understand the importance of maintaining batch quality. Well-trained and motivated employees are more likely to follow quality procedures and contribute to better product outcomes.
8. Lean and Six Sigma Principles:
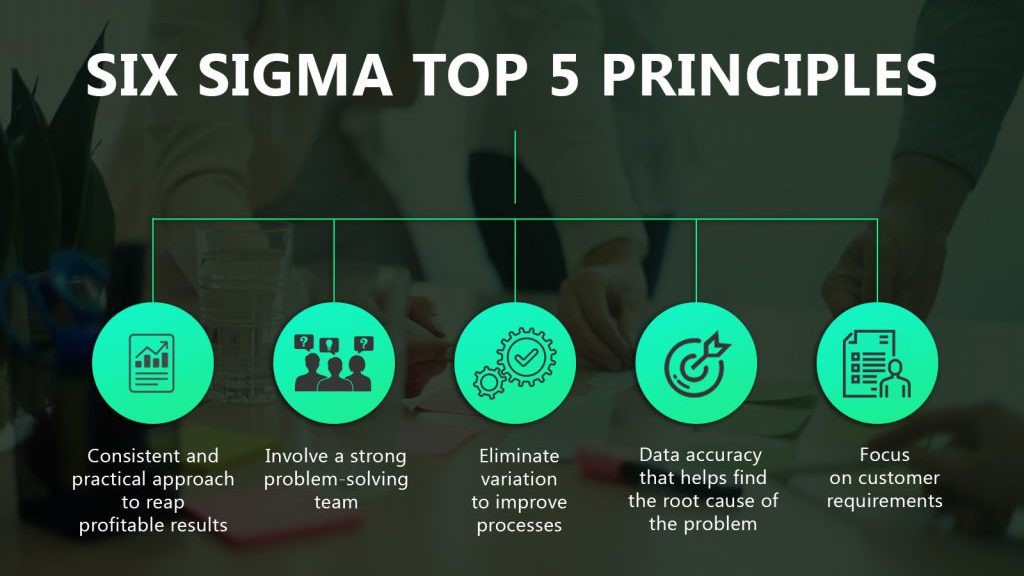
Six Sigma Principles
Consider implementing Lean and Six Sigma principles in your production processes. These methodologies focus on eliminating waste and reducing variation, which can lead to improved batch quality.
9. Technology and Automation:
Leverage technology and automation to enhance batch quality control. Automated systems can perform repetitive tasks with precision, reducing the chances of human error.
10. Continuous Improvement:
Adopt a culture of continuous improvement. Encourage employees to provide feedback and suggestions for enhancing batch quality. Small, incremental improvements can add up to significant gains over time.
11. Customer Feedback:
Customer feedback is a valuable source of information regarding batch quality. Actively seek and listen to customer input, and use it to make necessary improvements.
12. Batch Traceability:
Implement batch traceability systems that allow you to track and trace the production history of each batch. This ensures accountability and facilitates quick response to quality issues.
13. Risk Management:
Develop a risk management plan that identifies potential quality risks and outlines strategies for mitigating them. Being proactive in risk management can prevent bad batches from occurring.
14. Cost Analysis:
Analyze the cost of poor quality, including the expenses associated with producing and addressing bad batches. This analysis can provide a clear picture of the financial impact of batch quality issues.
15. Documentation and Records:
Maintain thorough documentation and records of all production processes and quality control activities. This documentation serves as a reference for evaluating batch quality and ensuring compliance with quality standards.
Assessing and improving batch quality is an ongoing process that requires commitment, diligence, and a proactive approach. By setting clear standards, implementing quality control measures, conducting root cause analyses, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, you can minimize the occurrence of bad batches and enhance the reputation of your products. Remember that batch quality is not just about meeting industry standards but exceeding customer expectations. In the competitive world of manufacturing and production, superior batch quality can be a key differentiator and a driver of long-term success.