Understanding Mixed Genital Flora Isolated: Causes and Implications
Mixed genital flora isolated is a term often encountered in medical contexts, particularly in the field of microbiology and gynecology. This phrase refers to the presence of multiple types of microorganisms in the genital tract. In this article, we will delve into what mixed genital flora isolated means, the possible causes behind its occurrence, and its clinical significance.
Mixed genital flora isolated
1. Defining Mixed Genital Flora Isolated: A Microbiological Perspective
Microbial Diversity: Mixed genital flora isolated refers to the detection of various microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, in the genital tract during laboratory testing.
Common Sites: It can occur in both males and females, affecting areas like the vagina, cervix, urethra, and even the penis.
2. Causes of Mixed Genital Flora Isolated: Factors Behind Its Occurrence
Natural Microbiome: The genital tract naturally contains a diverse range of microorganisms, including both beneficial and potentially harmful species.
Antibiotic Use: Taking antibiotics can disrupt the balance of the genital microbiome, leading to the isolation of mixed flora.
Sexual Activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce new microorganisms into the genital tract.
Poor Hygiene: Inadequate genital hygiene can contribute to changes in the microbial composition.
3. Clinical Significance: Isolated Mixed Genital Flora
Infection Risk: Mixed genital flora isolated can increase the risk of genital infections, such as bacterial vaginosis, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and yeast infections.
Symptoms: It may lead to symptoms like itching, discharge, discomfort, or pain in the genital area.
Pregnancy Complications: In pregnant individuals, mixed genital flora isolated can be associated with complications such as preterm birth.
4. Diagnosis and Testing: Detecting Mixed Genital Flora
Microbiological Cultures: Medical professionals use microbiological cultures to identify the specific microorganisms present in the genital tract.
Molecular Testing: Advanced techniques like PCR (polymerase chain reaction) can provide a more accurate assessment of microbial diversity.
5. Treatment and Management: Addressing Mixed Genital Flora
Antibiotics: In cases where mixed genital flora isolated is causing infections, antibiotics may be prescribed to target the specific microorganisms involved.
Probiotics: Some individuals use probiotics to help restore a healthy genital microbiome.
Hygiene Practices: Maintaining proper genital hygiene can reduce the risk of disruptions to the microbiome.
6. Prevention: Strategies for Maintaining Genital Health
Safe Sexual Practices: Practicing safe sex can reduce the risk of introducing new microorganisms into the genital tract.
Hygiene Education: Promoting good genital hygiene habits can help individuals maintain a balanced microbiome.
Regular Check-Ups: Routine gynecological or urological check-ups can help detect and address any issues related to genital flora.
7. Future Research and Insights: Advancements in Microbiome Science
Microbiome Research: Ongoing research into the genital microbiome may provide further insights into its composition and functions.
Personalized Medicine: Understanding an individual's genital microbiome could lead to more personalized medical approaches in the future.
Complex Microbial Ecosystem: The genital tract is host to a complex ecosystem of microorganisms, and the presence of mixed genital flora isolated is a common occurrence.
Medical Attention: If symptoms or complications arise, seeking medical attention and following prescribed treatments is crucial for maintaining genital health.
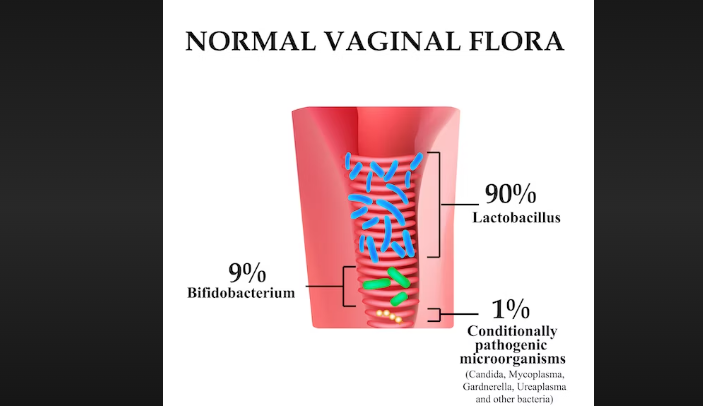
Normal Vaginal Flora
In conclusion, mixed genital flora isolated is a term used in medical contexts to describe the presence of diverse microorganisms in the genital tract. While it is a natural occurrence to some extent, imbalances can lead to health issues. Understanding the causes, clinical significance, and management options can help individuals maintain genital health and seek appropriate medical care when needed.