Male and Female Leopard Geckos: A Comprehensive Guide
Leopard geckos, native to the arid regions of Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India, have become beloved pets around the world. Their distinctive spotted patterns and docile nature make them a favorite among beginners and experienced reptile keepers alike.
Physical Differences
1. Size and Shape:
Male leopard geckos are generally smaller and more slender than females. Males usually measure around 8 to 10 inches in length, while females can reach lengths of 7 to 8 inches.
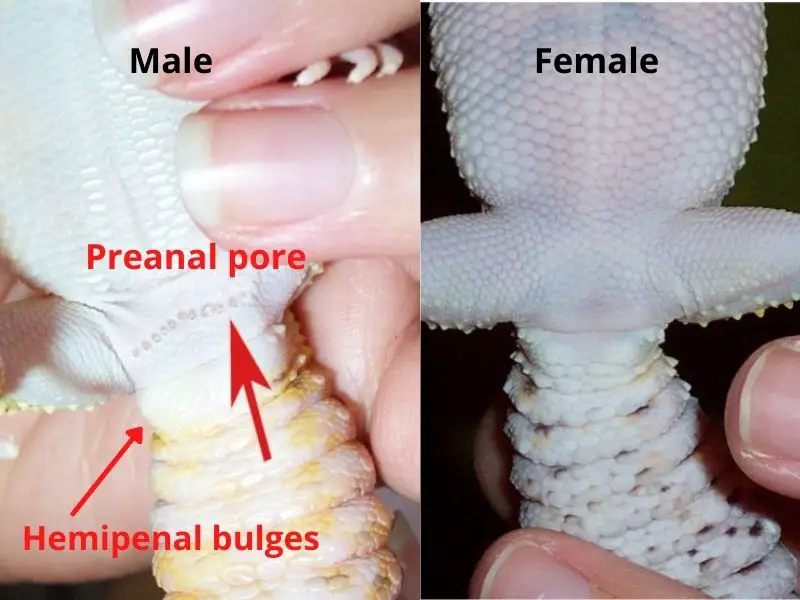
2. Hemipenal Bulges:
One of the most prominent distinguishing features is the presence of hemipenal bulges at the base of the tail in males. These bulges are absent in females, making it a reliable method of sexing adult leopard geckos.
3. Pore Placement:
Males possess preanal pores located just above the vent, which release a waxy substance used in marking territory. Female geckos lack these pores.

Leopard gecko
Behavioral Differences
1. Vocalizations:
While leopard geckos are generally quiet, males can occasionally make soft clicking or chirping sounds, especially during mating rituals or when feeling threatened. Females do not exhibit this behavior.
2. Territoriality:
Male geckos tend to be more territorial and can become aggressive towards other males, particularly during the breeding season. Females are usually more social and can often coexist peacefully in the same enclosure.
Housing and Care
1. Enclosure Setup:
Creating a suitable habitat is crucial for the health and well-being of your leopard geckos. Provide a spacious enclosure with appropriate hiding spots, a warm basking area, and a moist hide for shedding.
2. Temperature and Lighting:
Maintain a temperature gradient in the enclosure, with a basking spot around 88-92°F (31-33°C) and a cooler side around 75-80°F (24-27°C). Use a full-spectrum UVB light to aid in calcium metabolism.
3. Diet and Feeding:
Leopard geckos are insectivores, primarily consuming crickets, mealworms, and other appropriately sized insects. Dust the prey with calcium and vitamin supplements before feeding.
Difference Between Male And Female Leopard Geckos
Breeding Considerations
1. Mating Behavior:
During the breeding season, males will exhibit courtship behaviors such as head bobbing and tail waving to attract females. Successful copulation is often followed by egg-laying.
2. Egg Incubation:
If breeding is your goal, provide a separate egg-laying container with a mixture of vermiculite and water for females. Incubate the eggs in a controlled environment with temperatures around 80-85°F (27-29°C) to ensure proper development.
Understanding the distinctions between male and female leopard geckos is essential for their optimal care and potential breeding endeavors. By paying attention to physical attributes, behavior, and specific care requirements, you can provide a suitable and enriching environment for these captivating reptile companions. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned reptile enthusiast, the joys of keeping leopard geckos are boundless, as you witness their unique personalities and behaviors unfold in your care.