How Much Do Engines Weigh: A Comprehensive Guide
Engines play a crucial role in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and marine. One key factor to consider when working with engines is their weight. Understanding the weight of engines is essential for transportation, design, and safety purposes. In this article, we will explore the weight of engines, factors affecting their weight, and provide examples across different types of engines.
Engine weight
1.Importance of Knowing Engine Weight:
Knowing the weight of an engine is vital for several reasons.
First, it helps determine the suitability of an engine for a particular application. Whether it's a car, airplane, or ship, understanding engine weight ensures proper functioning and performance.
Additionally, engine weight affects fuel efficiency, payload capacity, and overall design considerations.
2.Factors Affecting Engine Weight:
Several factors influence the weight of an engine. These factors vary depending on the engine type, size, and purpose. Let's delve into some of the primary factors:
a) Engine Type:
Different types of engines have varying weights. For instance, internal combustion engines, including gasoline and diesel engines, generally weigh more than electric motors due to their complex internal components.
b) Engine Size:
Engine size is directly proportional to its weight. Larger engines tend to be heavier as they require more materials and components to function effectively.
c) Materials Used:
The choice of materials impacts engine weight significantly. Lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys and carbon composites reduce the overall weight, while heavy materials like cast iron increase it.
d) Features and Accessories:
Additional features and accessories like turbochargers, intercoolers, and emission control systems contribute to engine weight. These components enhance performance but also add extra mass.

Engine weight
3.Engine Weight Comparison:
Let's compare the weights of engines across different categories:
a) Automotive Engines:
-
Gasoline Engine: On average, a small gasoline engine for a compact car weighs around 200-300 kilograms (440-660 pounds). Larger engines for trucks or high-performance vehicles can weigh up to 500 kilograms (1100 pounds) or more.
-
-
Diesel Engine: Diesel engines are generally heavier than gasoline engines due to their robust construction. A typical diesel engine for a medium-sized truck weighs between 700-1000 kilograms (1540-2200 pounds).
-
b) Aircraft Engines:
-
Piston Engine: Small aircraft piston engines can weigh around 100-200 kilograms (220-440 pounds). However, larger piston engines for commercial airplanes can weigh several tons.
-
-
Jet Engine: Jet engines, commonly used in commercial airliners, vary significantly in weight depending on their size and power output. Smaller jet engines weigh around 500-1500 kilograms (1100-3300 pounds), while larger ones can exceed 10,000 kilograms (22,000 pounds).
-
c) Marine Engines:
-
Outboard Motor: Small outboard motors for boats generally weigh between 10-100 kilograms (22-220 pounds). Larger marine engines for ships and vessels can weigh several tons.
-
-
Ship Engine: Ship engines are among the heaviest engines. A large ship engine can weigh anywhere from 1000 to 5000 tons or more.
-
4.Engine Weight Optimization:
Reducing engine weight can offer several advantages, including improved fuel efficiency and increased payload capacity. Engine manufacturers employ various optimization techniques, such as:
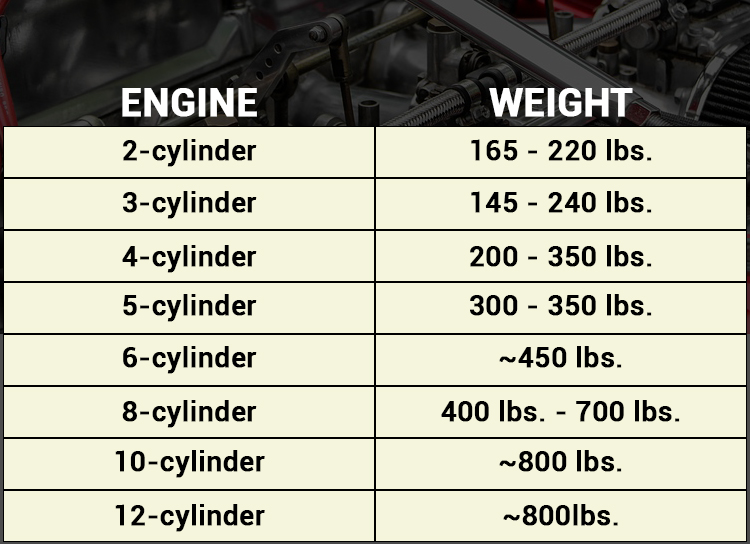
Engine weight
a) Lightweight Materials:
Using lightweight materials like titanium, carbon fiber, and high-strength alloys can significantly reduce engine weight without compromising performance.
b) Compact Design:
Designing engines with smaller footprints and compact internal components helps minimize weight while maintaining functionality.
c) Advanced Manufacturing Techniques:
Employing advanced manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing (3D printing) allows for complex designs, lightweight structures, and reduced material waste.
Understanding the weight of engines is crucial for various industries. By considering factors such as engine type, size, materials used, and additional accessories, we can estimate their weights more accurately. Whether it's automotive, aerospace, or marine engines, knowing their weights helps in making informed decisions regarding performance, design, and safety considerations.