Which Element is Found in Both DNA and Protein? Exploring the Role of Sulfur, Sodium, Nitrogen, and Chlorine
In the world of biology, DNA and proteins play vital roles in the functioning of living organisms. Both DNA and proteins are composed of various elements, each contributing to their unique properties and functions. This article aims to explore the presence of sulfur, sodium, nitrogen, and chlorine in both DNA and proteins, shedding light on their significance in these fundamental biomolecules.
Sulfur: Linking DNA and Proteins
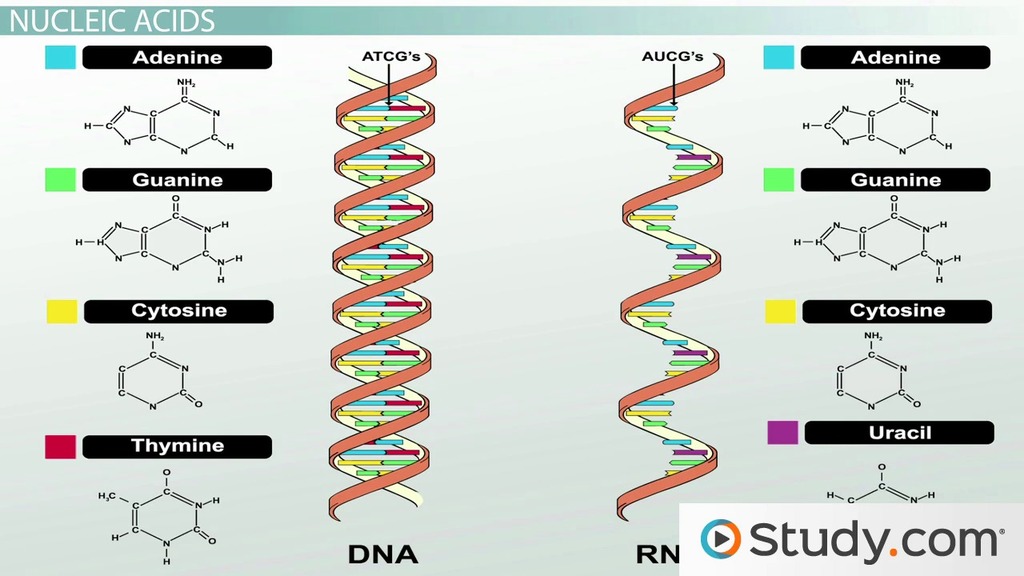
DNA
1.1 The Importance of Sulfur in DNA
Sulfur is not a major component of DNA; however, it plays a crucial role in the structural integrity of this genetic material. The sulfur-containing amino acid cysteine forms disulfide bridges within and between DNA strands, stabilizing the double helix structure and promoting DNA stability.
1.2 Sulfur's Role in Proteins
Sulfur is an essential element in proteins due to the presence of sulfur-containing amino acids, such as cysteine and methionine. These amino acids play critical roles in protein structure and function. Cysteine residues form disulfide bonds, contributing to protein folding, stability, and intermolecular interactions.
Sodium: Maintaining Cellular Balance
sodium
2.1 Sodium's Role in DNA
Sodium does not have a direct role in DNA structure or function. However, it plays a significant role in maintaining the ionic balance within cells, which indirectly influences DNA stability and replication.
2.2 Sodium's Role in Proteins
Sodium ions are involved in protein structure and function. They contribute to the stability and conformation of certain proteins, particularly those associated with cell membranes. Sodium also plays a crucial role in the regulation of enzyme activity, cell signaling, and protein-protein interactions.
Nitrogen: Essential for Nucleotides and Amino Acids
3.1 Nitrogen's Role in DNA
Nitrogen is a primary component of DNA's building blocks, nucleotides. Nitrogenous bases, namely adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, form the genetic code. The hydrogen bonding between these bases holds the two DNA strands together, forming the characteristic double helix structure.
3.2 Nitrogen's Role in Proteins
Nitrogen is an essential component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Amino acids contain amino groups (-NH2) that are composed of nitrogen. These amino groups participate in peptide bond formation, linking amino acids together and forming the protein's primary structure.
Chlorine: A Modulator of DNA Stability
4.1 Chlorine's Role in DNA
Chlorine does not have a direct role in DNA structure. However, it can affect DNA stability through interactions with other elements or molecules. Chlorine-containing compounds can modify DNA bases or disrupt hydrogen bonding, leading to changes in DNA structure and function.
4.2 Chlorine's Role in Proteins
Chlorine does not have a significant role in protein structure or function. However, some proteins, such as chloride channels, are specifically involved in transporting chloride ions across cell membranes, maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating various physiological processes.
In conclusion, sulfur, sodium, nitrogen, and chlorine are elements that can be found in both DNA and proteins, albeit with different roles and levels of significance. Sulfur contributes to the stability and structure of DNA and proteins, while sodium helps maintain cellular balance and influences protein conformation. Nitrogen is essential for the building blocks of DNA and proteins, whereas chlorine's effects on DNA and proteins are more indirect. Understanding the presence and functions of these elements in DNA and proteins provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of living organisms.