Which Part of a DNA Molecule is Responsible for the Direct Coding of Specific Traits in an Organism?
In the field of genetics, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) plays a crucial role in determining the traits and characteristics of living organisms. Within the DNA molecule, there is a specific part responsible for encoding the information needed for the development and expression of traits. In this article, we will explore the role of this essential component and its significance in genetic inheritance.
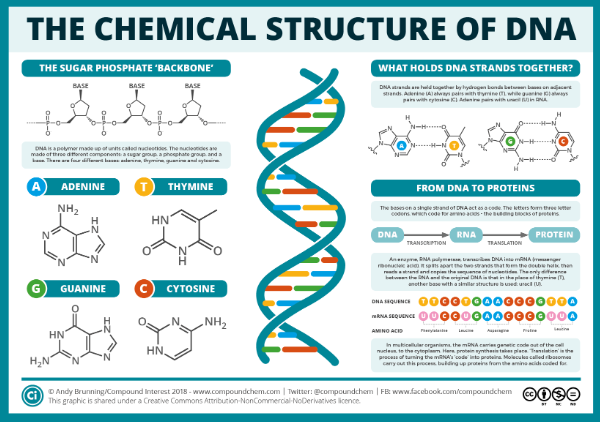
The Chemical Structure of DNA
1. Understanding DNA:
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that carries the genetic instructions necessary for the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms.
It consists of four nucleotide bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The sequence of these bases determines the genetic code.
2. Structure of DNA:
DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes, which are located in the nucleus of a cell.
Each chromosome contains long strands of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones.
The DNA molecule is shaped like a twisted ladder, with the bases forming the rungs and the sugar-phosphate backbone forming the sides.
3. Genes and Traits:
Genes are specific segments of DNA that contain the instructions for producing proteins.
Proteins, in turn, play a vital role in the development and functioning of an organism, including the expression of traits.
Different combinations of genes determine an organism's unique set of traits, such as eye color, height, and hair texture.
4. The Role of Genes in Trait Expression:
Within the DNA molecule, the coding for specific traits is carried out by sequences of bases known as exons.
Exons are the parts of genes that directly code for proteins or functional RNA molecules.
They contain the instructions necessary for the synthesis of specific proteins that contribute to trait development.
5. Transcription and Translation:
The process by which genetic information is used to create proteins is called gene expression.
It involves two main steps: transcription and translation.
During transcription, an enzyme called RNA polymerase reads the DNA sequence and produces a complementary RNA molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA).
The mRNA then undergoes translation, where it is read by ribosomes, and the encoded instructions are used to assemble the corresponding protein.
6. Genetic Variation and Alleles:
Genetic variation occurs due to differences in the DNA sequences of individuals. Within a population, different versions of a gene are called alleles. Alleles can have variations in their coding sequences, which may result in different traits or variations of a particular trait.
7. The Significance of Mutations:
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can occur naturally or due to external factors. They can alter the coding sequence of genes, leading to changes in the traits expressed by an organism. Mutations play a crucial role in evolution, as they introduce new genetic variations that can be selected for or against in a changing environment.
All part of a DNA
The part of a DNA molecule responsible for the direct coding of specific traits in an organism is the exons within genes. These sequences of bases contain the instructions for the synthesis of proteins that contribute to trait development. Understanding the role of genes and their coding sequences is essential for unraveling the complexity of genetic inheritance and the expression of traits in living organisms.