Exploring Storage Capacity: What is Bigger Than a Terabyte?
As technology advances and data storage becomes increasingly vital, it's important to understand the different units of measurement used to quantify digital information. While most of us are familiar with terms like kilobyte, megabyte, and terabyte, you may wonder what comes next in terms of storage capacity. In this informative article, we will delve into the topic and explore what is bigger than a terabyte. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of digital storage and discover larger units of measurement.
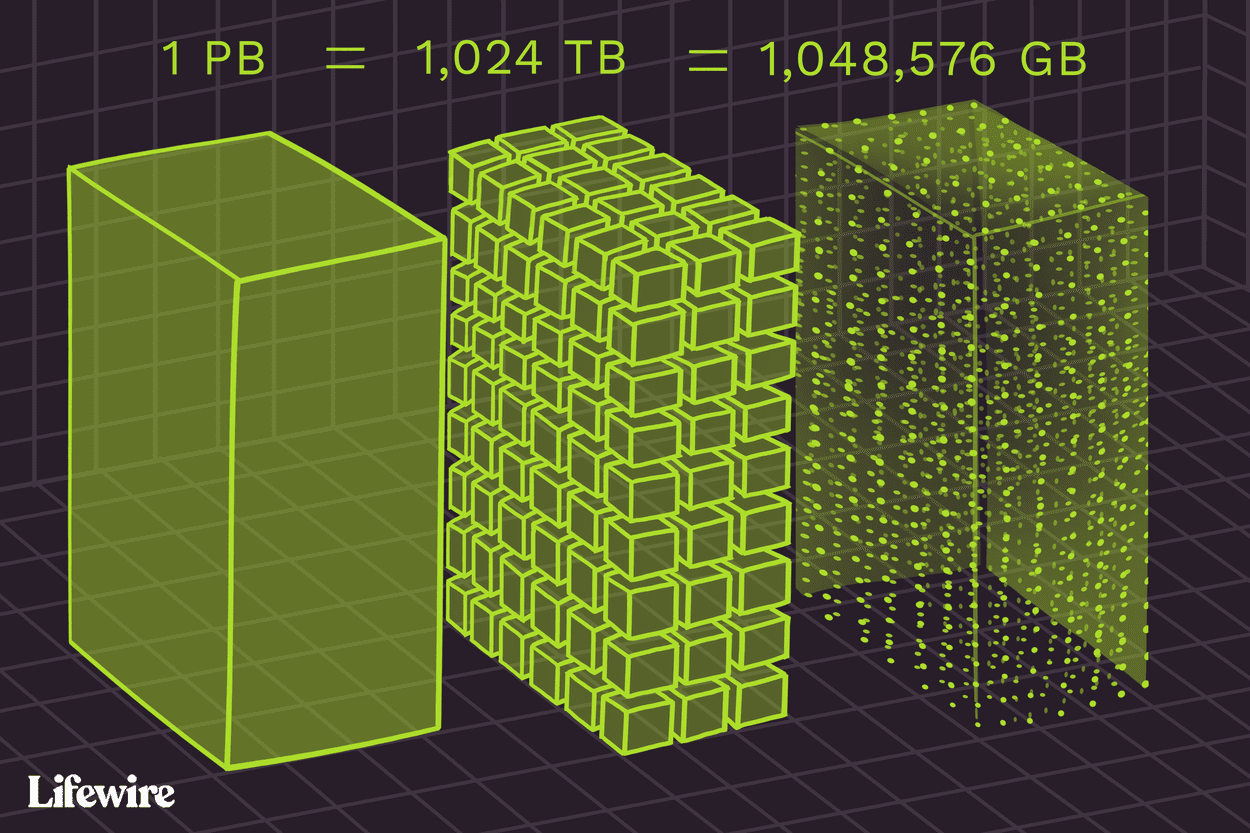

1PB= 1024TB
1. Understanding Data Storage Units:
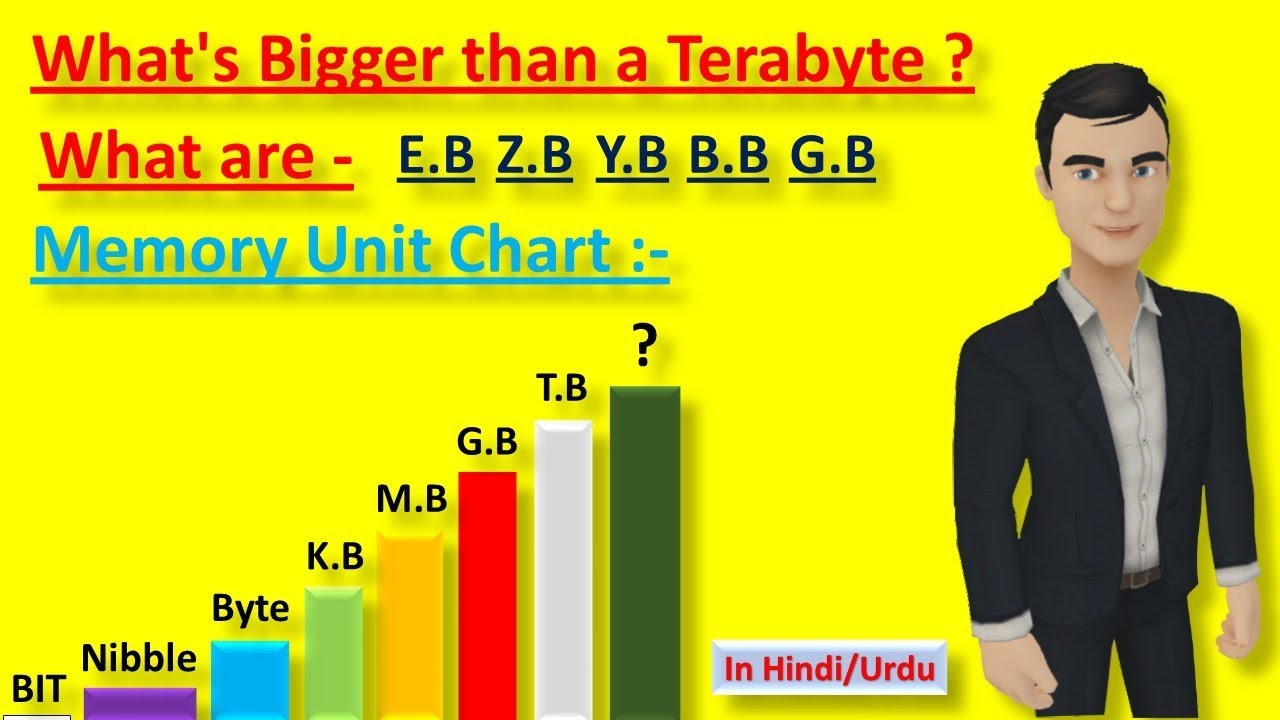
a. Bits and Bytes: The fundamental building blocks of digital information are bits (binary digits) and bytes (a collection of bits). A byte typically consists of 8 bits.
b. Decimal vs. Binary: It's important to note the difference between decimal and binary systems of measurement. In decimal, each unit increases by a factor of 1,000, while in binary, it increases by a factor of 1,024.
2. Common Data Storage Units:
a. Kilobyte (KB): Equal to 1,000 bytes or 1,024 bytes in binary.
b. Megabyte (MB): Equal to 1,000 kilobytes or 1,024 kilobytes in binary.
c. Gigabyte (GB): Equal to 1,000 megabytes or 1,024 megabytes in binary.
d. Terabyte (TB): Equal to 1,000 gigabytes or 1,024 gigabytes in binary.
3. Units Larger Than a Terabyte:
a. Petabyte (PB): Equal to 1,000 terabytes or 1,024 terabytes in binary. A petabyte represents a massive amount of data and is commonly used in large-scale storage systems, such as data centers.
b. Exabyte (EB): Equal to 1,000 petabytes or 1,024 petabytes in binary. An exabyte is a substantial unit of measurement often associated with massive data storage, scientific research, and high-performance computing.
c. Zettabyte (ZB): Equal to 1,000 exabytes or 1,024 exabytes in binary. A zettabyte represents an astronomical amount of data and is often used in discussions about global data consumption and storage capacity.
d. Yottabyte (YB): Equal to 1,000 zettabytes or 1,024 zettabytes in binary. A yottabyte is the largest recognized unit of measurement for data storage and is virtually inconceivable in terms of the amount of information it represents.
4. Real-World Applications:
a. Big Data: The advent of big data has increased the need for storage units beyond terabytes. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and technology often deal with massive amounts of data that require petabyte or even exabyte storage capacities.
b. Scientific Research: Fields like astronomy, genomics, and climate modeling generate enormous datasets that require storage units larger than a terabyte to accommodate their research findings.
5. Technological Advancements:
Future Possibilities: As technology continues to evolve, the need for even larger storage capacities may arise. Scientists and researchers are continually exploring new materials and techniques to push the boundaries of data storage.
What bigger than a terabyte?
While terabytes are widely known and used in everyday life, it's fascinating to explore what lies beyond this common unit of measurement. Petabytes, exabytes, zettabytes, and yottabytes represent the next frontiers in data storage. As the digital landscape expands and data becomes increasingly vital, understanding these larger storage units provides insights into the scale and magnitude of information being generated and managed worldwide. Embrace the possibilities of big data and stay informed about the ever-expanding world of digital storage.