Understanding the Relationship Between Energy, Power, Force, and Motion: Exploring the Ability to Do Work
In the field of physics, various terms are used to describe the fundamental aspects of the physical world. Energy, power, force, and motion are four important concepts that are closely related and play a crucial role in understanding the ability to do work. This article will delve into each of these terms, exploring their definitions, interconnections, and real-world applications.
I. Energy:
Energy can be defined as the capacity to do work. It is a fundamental property of matter and exists in different forms such as kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, and more. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can be converted from one form to another. This concept is governed by the law of conservation of energy.
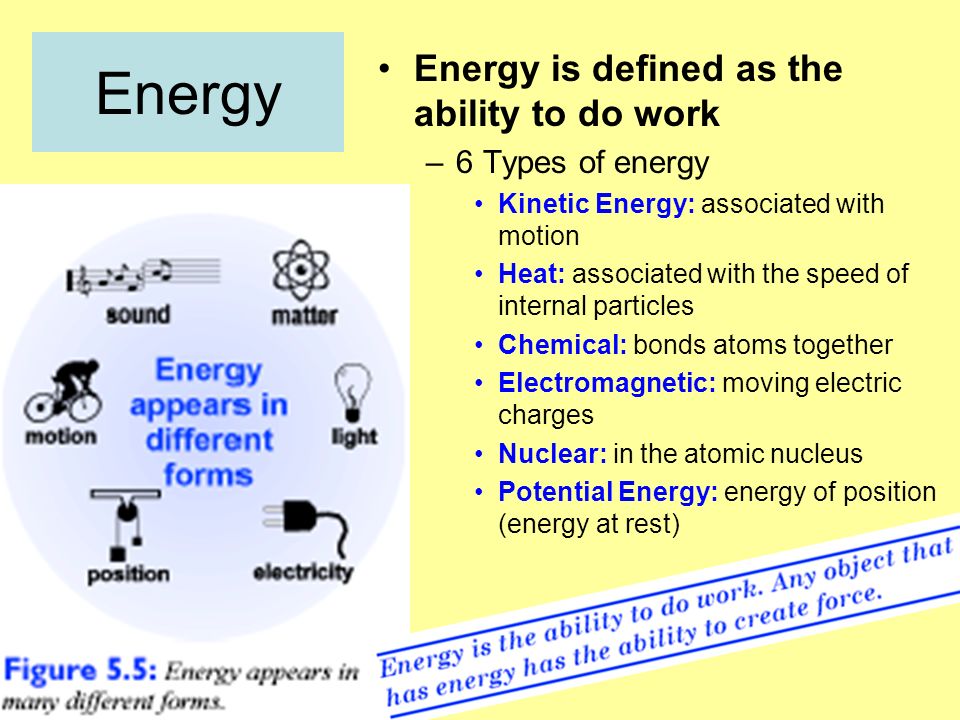
Energy
II. Power:
Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. It quantifies how quickly work is accomplished. Power is measured in watts (W) and is calculated by dividing the amount of work done by the time taken to do it. In simple terms, power determines how fast energy is converted or transferred.
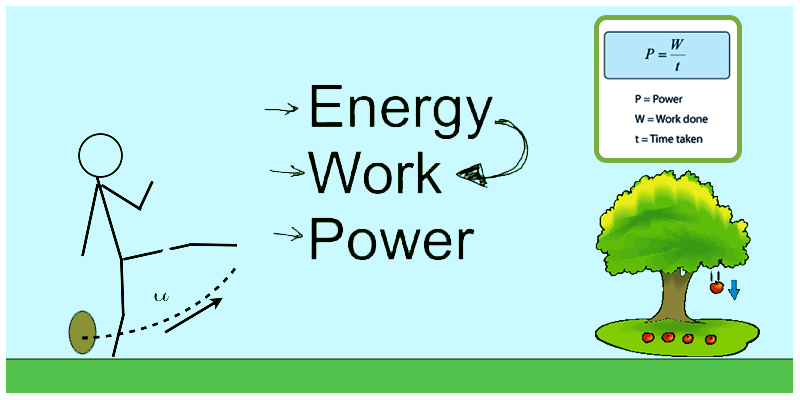
Power
III. Force:
Force refers to a push or pull that can change the state of motion of an object. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. Force is measured in newtons (N) and is related to the mass and acceleration of an object through Newton's second law of motion, F = ma.
IV. Motion:
Motion is the change in position of an object over time. It can be described in terms of speed, velocity, and acceleration. Speed refers to the rate at which an object covers distance, while velocity takes into account both speed and direction. Acceleration, on the other hand, refers to the rate at which an object's velocity changes.
Comparison Table:
| Term | Definition | Unit of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | The capacity to do work | Joule (J) |
| Power | The rate at which work is done or energy is transferred | Watt (W) |
| Force | A push or pull that can change an object's motion | Newton (N) |
| Motion | Change in position of an object over time | - |
V. Interconnections:
Energy, power, force, and motion are intricately interconnected. Energy is required to perform work, and power determines how quickly the work is done or energy is transferred. Force is responsible for causing a change in motion, and motion itself is the result of a force acting upon an object. Thus, energy, power, force, and motion are interdependent and contribute to the ability to do work.
VI. Real-World Applications:
Understanding the relationship between energy, power, force, and motion has numerous practical applications.
For example:
- In the field of engineering, this knowledge is crucial for designing efficient machines and systems.
- In sports, energy, power, force, and motion play a significant role in analyzing and improving athletic performance.
- Renewable energy technologies rely on the conversion of natural resources into usable energy forms, utilizing the principles of energy, power, force, and motion.
Energy, power, force, and motion are key concepts in physics that help us understand the ability to do work. Energy provides the capacity, power quantifies the rate, force causes changes, and motion represents the result. By comprehending the interconnections between these terms, we gain valuable insights into the physical world and its applications in various domains.