How Many Neutrons Does Cl Have: Unveiling the Neutron Count of Chlorine
Chlorine, a chemical element known for its disinfectant properties and presence in common table salt, holds a significant place in the periodic table. While many are familiar with its role in sanitation and chemistry, questions about its atomic structure often arise. In this article, we will explore one such question: "How many neutrons does Cl have?" We will delve into the atomic composition of chlorine, its isotopes, and the importance of neutrons in understanding its behavior.
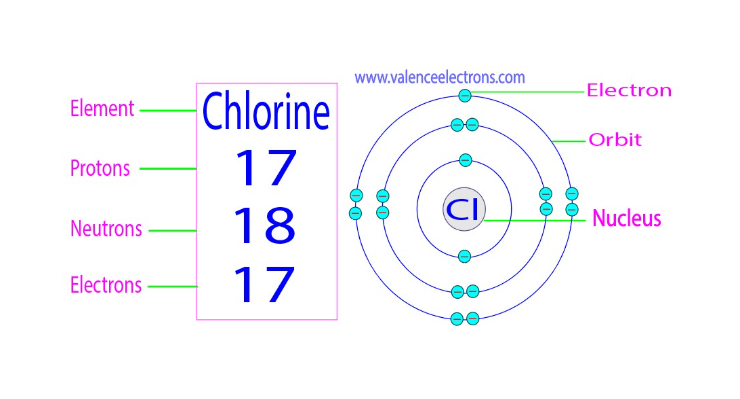
Neutrons have 18 in Cl
1. Chlorine: An Elemental Overview
Before we delve into the neutron count, let's establish some fundamental information about chlorine:
-
Atomic Symbol: Chlorine is represented by the chemical symbol "Cl."
-
-
Atomic Number: Chlorine has an atomic number of 17, which signifies the number of protons in its nucleus. This also determines its place in the periodic table.
-
-
Electron Configuration: Chlorine's electron configuration is 2-8-7, meaning it has 17 electrons distributed across its energy levels.
2. The Role of Neutrons
Neutrons are subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom, alongside protons.
While protons carry a positive charge, neutrons are electrically neutral. Neutrons play a crucial role in determining an element's stability, isotope variations, and nuclear properties.
3. Neutrons in Chlorine
To determine the number of neutrons in an atom of chlorine, we need to consider its isotopes. Isotopes are variants of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Chlorine has two stable isotopes: chlorine-35 and chlorine-37.
-
Chlorine-35: This isotope of chlorine has 18 neutrons. Its atomic mass is approximately 35 atomic mass units (u).
-
-
Chlorine-37: Chlorine-37 has 20 neutrons, making it slightly heavier than chlorine-35. Its atomic mass is approximately 37 u.
4. Significance of Neutron Count
The number of neutrons in an isotope affects its stability and behavior.
Isotopes with an excess or deficiency of neutrons can be unstable and undergo radioactive decay to achieve a more stable neutron-to-proton ratio.
5. Chlorine in Daily Life
Chlorine and its compounds have various applications in everyday life:
-
Disinfection: Chlorine-based compounds are widely used to disinfect drinking water and swimming pools, eliminating harmful microorganisms.
-
-
Chemical Manufacturing: Chlorine is an essential component in the production of chemicals such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and chlorinated solvents.
-
-
Food Processing: Chlorine is used in the food industry to sanitize equipment and ensure food safety.

What are the isotopes of chlorine?
In conclusion, chlorine, with its atomic number of 17, has varying numbers of neutrons in its isotopes. Chlorine-35 has 18 neutrons, while chlorine-37 has 20 neutrons. Understanding the neutron count of an element is essential in comprehending its isotopic variations and behavior. Chlorine, known for its disinfectant properties and presence in everyday products, is a versatile element with a rich chemistry. Its atomic structure, including the neutron count, contributes to its wide range of applications in our daily lives and various industries.