What Determines the Speed at Which Data Travels? A Comprehensive Exploration
In today's digitally connected world, the speed at which data travels has become a critical factor in determining the efficiency of various online activities. From browsing the web and streaming media to uploading and downloading files, understanding the factors that influence data transfer speeds is essential. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of data transmission and explore the key determinants that impact the speed of data travel. By unraveling these factors, we can gain insights into optimizing data transfer for improved online experiences.
I. Network Bandwidth
One of the primary factors affecting data transmission speed is network bandwidth.
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted through a network within a given time frame.
It is typically measured in bits per second (bps) or its derivatives like kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or even gigabits per second (Gbps).
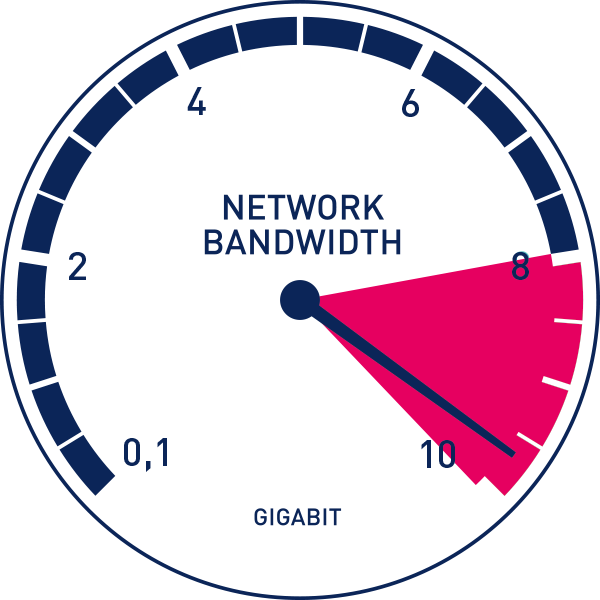
Network bandwidth
Network bandwidth is influenced by several factors, including the capacity of the network infrastructure, the quality and reliability of network components, and the congestion level.
Higher bandwidth allows for faster data transmission, enabling larger amounts of data to be transferred in a shorter duration.
II. Latency
Latency, often referred to as network delay, is another crucial factor affecting data travel speed.
It represents the time taken for a data packet to travel from the source to the destination.
Latency can be influenced by various elements, including the distance between the sender and receiver, the number of network hops, and the processing time at each network node.
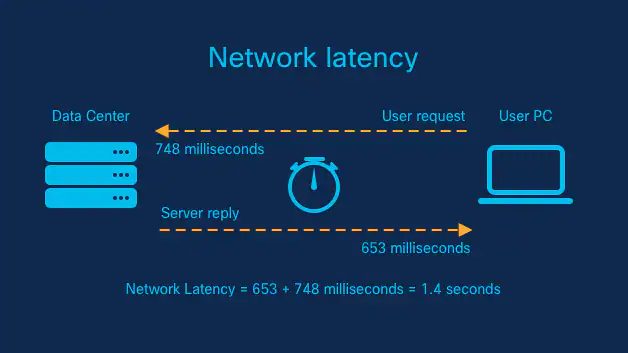
Latency
Latency is typically measured in milliseconds (ms). High latency can cause delays in data transfer, leading to slower speeds and increased waiting times.
To reduce latency, optimizing network routing, minimizing the number of network hops, and using advanced networking technologies, such as fiber optic cables, can be employed.
III. Transmission Medium
The transmission medium plays a significant role in determining data travel speed.
Different mediums have distinct characteristics that impact the speed and quality of data transmission.
Common transmission mediums include copper cables, fiber optics, and wireless connections.
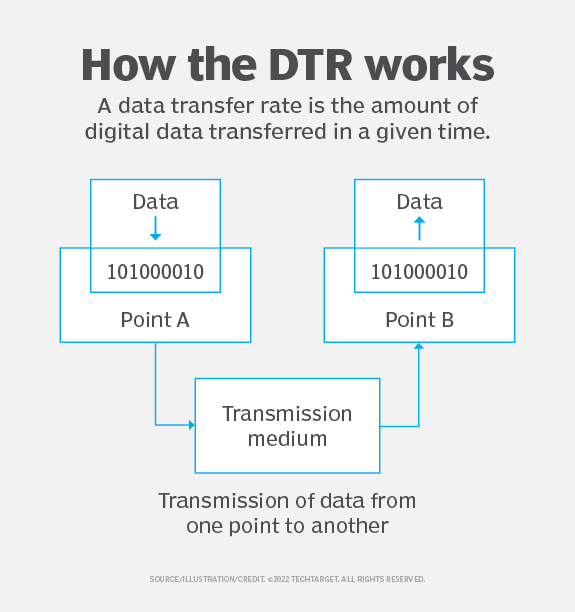
Transmission Medium
Copper cables, although widely used, have limitations in terms of data transmission speed and distance.
Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, offer significantly higher bandwidth and lower latency, making them ideal for long-distance data transmission.
Wireless connections, such as Wi-Fi or cellular networks, provide convenience but may have limitations in terms of bandwidth and potential interference.
IV. Network Congestion
Network congestion refers to a state where the demand for network resources exceeds the available capacity.
When multiple users share the same network infrastructure, congestion can occur, leading to slower data transfer speeds.
Factors contributing to network congestion include high user traffic, inefficient network management, and insufficient network infrastructure.
To alleviate network congestion and enhance data transfer speeds, various techniques can be employed.
These include traffic shaping, prioritizing critical data, implementing Quality of Service (QoS) measures, and upgrading network infrastructure to handle higher traffic volumes.
The speed at which data travels is influenced by multiple factors, including network bandwidth, latency, transmission medium, and network congestion. Understanding these determinants is crucial for optimizing data transfer speeds and ensuring efficient online experiences. By considering network upgrades, employing advanced transmission technologies, and implementing effective network management strategies, individuals and organizations can strive for faster data travel and better connectivity. As technology continues to advance, it is essential to stay informed about the factors influencing data transmission to adapt and optimize our digital interactions in an increasingly interconnected world.