Unveiling the Chemistry of 2-Methylbutane
In the realm of organic chemistry, hydrocarbons form the foundation of various compounds, and among them, 2-Methylbutane stands as an important member. Also known as isopentane, this hydrocarbon plays a significant role in the world of science and industry. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore 2-Methylbutane, its properties, uses, and its relevance in the field of chemistry.
1. What is 2-Methylbutane?
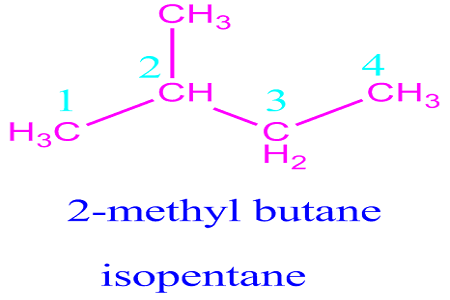
2-Methylbutane
2-Methylbutane, with its chemical formula C5H12, is an organic compound classified as an isomer of pentane.
Its structure features a branched chain, distinguishing it from its straight-chain counterparts. Understanding its molecular structure is crucial to comprehending its properties and applications.
2. Chemical Structure and Isomerism
To grasp the significance of 2-Methylbutane, we must delve into its chemical structure and the concept of isomerism.
This hydrocarbon's branched structure sets it apart from straight-chain pentane, resulting in distinct physical and chemical properties.
3. Physical Properties
2-Methylbutane exhibits intriguing physical properties that make it valuable in various applications:
a. State of Matter: At room temperature and standard atmospheric pressure, 2-Methylbutane exists as a colorless, flammable gas.
b. Boiling Point: One of its notable properties is its low boiling point, which makes it useful in numerous industrial processes.
c. Odor: It possesses a distinct odor that can be easily recognized.
4. Chemical Properties
Chemical Properties
Chemically, 2-Methylbutane participates in various reactions and processes:
a. Combustion: Like many hydrocarbons, 2-Methylbutane can undergo combustion reactions, releasing energy and producing carbon dioxide and water.
b. Halogenation: It reacts with halogens, such as chlorine and bromine, under suitable conditions.
5. Industrial and Scientific Applications
2-Methylbutane finds applications in a wide range of industries and scientific fields:
a. Laboratory Solvent: It serves as a common laboratory solvent due to its low boiling point and inert nature.
b. Octane Rating: In the automotive industry, 2-Methylbutane is used to determine the octane rating of gasoline, a critical factor in engine performance.
c. Calibration Gas: It is employed as a calibration gas in gas detectors and environmental monitoring instruments.
d. Refrigeration: In the past, it was used as a refrigerant, although its use has been largely phased out due to environmental concerns.
6. Safety and Handling
While 2-Methylbutane has several valuable applications, it is essential to understand safety precautions when handling this compound:
a. Flammability: 2-Methylbutane is highly flammable, and appropriate safety measures must be observed to prevent accidents.
b. Ventilation: When using it in a laboratory or industrial setting, proper ventilation is crucial to prevent the buildup of potentially harmful vapors.
c. Storage: It should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and incompatible substances.
7. Environmental Considerations
In recent years, environmental concerns have led to a shift away from the use of 2-Methylbutane in certain applications, particularly as a refrigerant.
This shift is part of broader efforts to reduce the environmental impact of various chemicals and compounds.
2-Methylbutane, with its unique chemical structure and properties, plays a vital role in the realms of chemistry, industry, and science. Its low boiling point, flammability, and versatility make it a valuable resource in laboratories, automotive engineering, and gas detection. However, its environmental impact and safety considerations also warrant attention. As our understanding of chemistry and environmental responsibility continues to evolve, so too will the applications and significance of 2-Methylbutane in our world.