Exploring the Number of Neutrons in Aluminum: A Comprehensive Guide
Aluminum, a versatile and widely used metal, plays a significant role in various industries. Its properties and behavior are of great interest to scientists and researchers, and one crucial aspect is the number of neutrons it contains. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of aluminum's atomic structure, focusing on the number of neutrons present in its nucleus. Understanding this fundamental aspect of aluminum can shed light on its properties and applications.
1. Aluminum's Atomic Structure
To comprehend the number of neutrons in aluminum, we must first grasp its atomic structure.
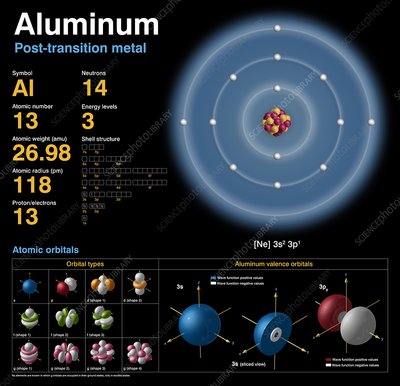
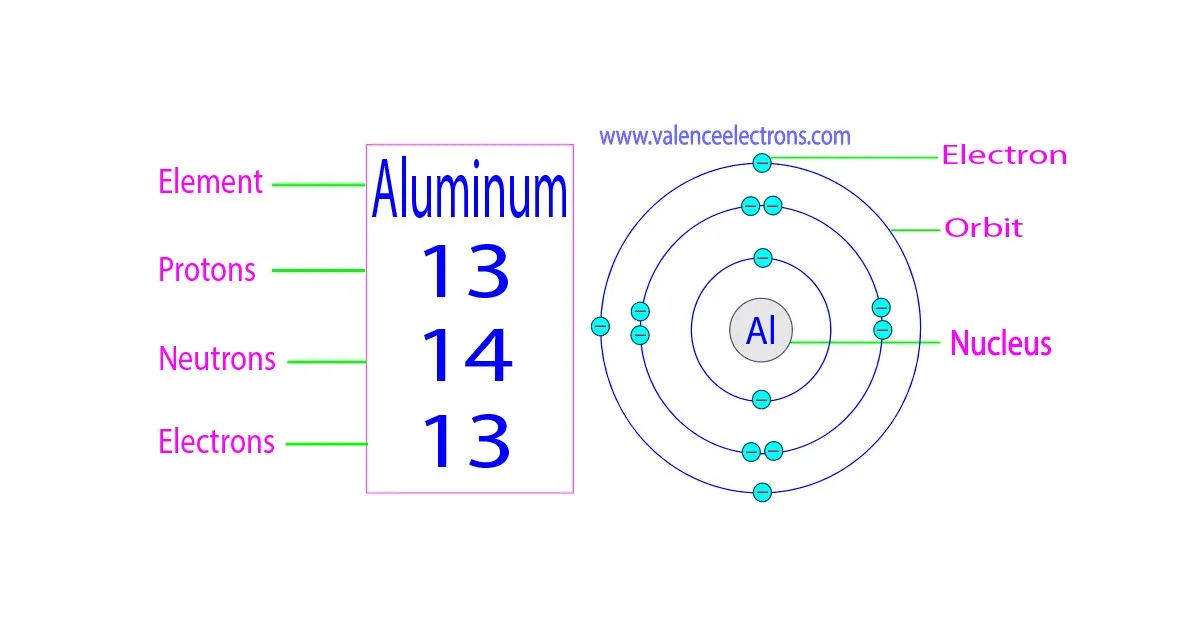
Aluminum is represented on the periodic table with the symbol 'Al' and has an atomic number of 13.
This means an aluminum atom contains 13 protons in its nucleus, giving it 13 electrons to balance the charge.
Aluminum
2. Neutrons in the Nucleus
Now, let's explore the number of neutrons in aluminum's nucleus. To find this, we'll need to calculate the neutron number, which can be determined by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass.
3. Atomic Mass of Aluminum
The atomic mass of aluminum is approximately 26.98 atomic mass units (u). This value represents the average mass of all naturally occurring aluminum isotopes, taking into account their abundance.
4. Calculating the Number of Neutrons
To calculate the number of neutrons in aluminum, use the following formula:
Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass - Atomic Number
For aluminum:
Number of Neutrons = 26.98 u - 13
Number of Neutrons = 13.98
Therefore, aluminum has approximately 13.98 neutrons in its nucleus.
Aluminum
5. Isotopes of Aluminum
Aluminum has several isotopes, but the most abundant and stable one is aluminum-27 (Al-27). This isotope accounts for nearly 100% of naturally occurring aluminum. Al-27 has 13 protons and 14 neutrons in its nucleus.
6. Significance of the Number of Neutrons in Aluminum
Understanding the number of neutrons in aluminum is crucial for several reasons.
a. Stability: The number of neutrons in an atom's nucleus influences its stability. Aluminum-27 is stable due to its balanced proton-to-neutron ratio.
b. Nuclear Properties: The number of neutrons affects the nuclear properties of aluminum, including its potential for nuclear reactions.
c. Applications: Knowledge of aluminum's atomic structure, including the number of neutrons, is vital in various applications, such as materials science, nuclear engineering, and metallurgy.
7. Other Aluminum Isotopes
While Al-27 is the most abundant isotope, other aluminum isotopes, such as Al-26 and Al-28, exist.
These isotopes are typically used in scientific research, particularly in radiometric dating and astrophysics.
In conclusion, the number of neutrons in aluminum plays a significant role in understanding its atomic structure and behavior. Aluminum-27, the most abundant isotope, has 14 neutrons in its nucleus, making it stable and suitable for various applications. This knowledge is essential for scientists, researchers, and engineers working with aluminum in diverse fields. By delving into the atomic properties of aluminum, we can unlock its full potential and expand our understanding of this remarkable element.