Unveiling the Valence Electrons in Calcium (Ca): Understanding Its Electron Configuration
In the realm of chemistry, the arrangement of electrons in an atom plays a fundamental role in determining its chemical properties and behavior. Calcium (Ca) is no exception. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of valence electrons in calcium, uncovering the number of valence electrons it possesses and its significance.
1. The Structure of an Atom
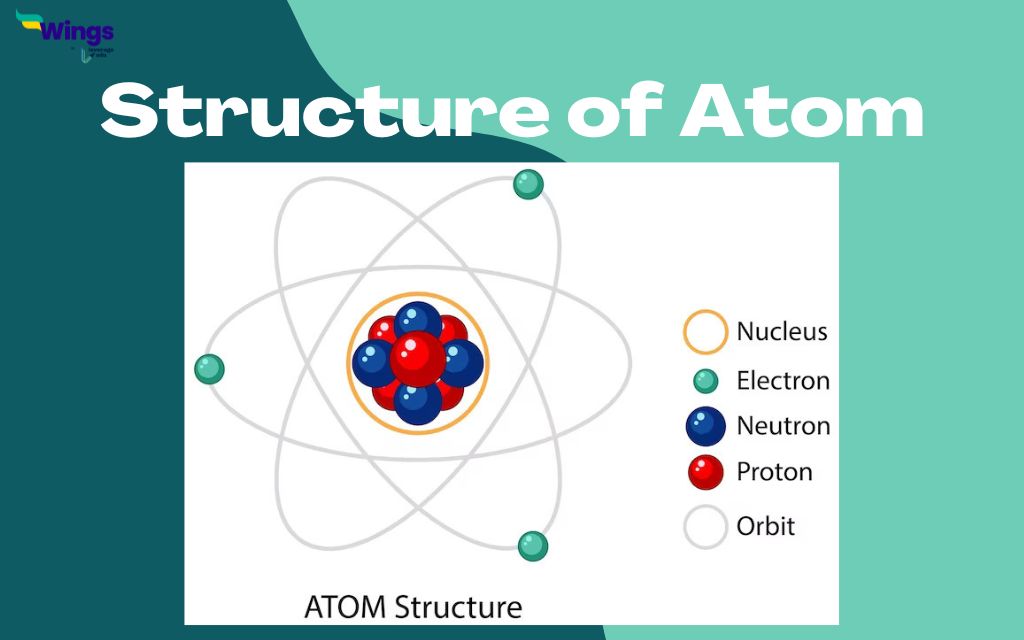
Structure of an Atom
Atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electron shells.
The outermost shell, known as the valence shell, is particularly important in chemical reactions.
2. Calcium: A Basic Overview
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol "Ca" and atomic number 20.
It belongs to the alkaline earth metals group in the periodic table and is known for its essential role in various biological processes.
3. Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of an atom describes how its electrons are distributed among different energy levels or orbitals. For calcium, the electron configuration is 1s² 2s² 2pⶠ3s² 3pⶠ4s².
4. Valence Electrons: The Key Players
Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost energy level of an atom.
These electrons are responsible for the atom's chemical properties and its interactions with other atoms.
5. The Valence Electrons of Calcium
Calcium has a total of 20 electrons, and its electron configuration reveals that it has 2 valence electrons in its outermost energy level, which is the 4s orbital.
6. Importance of Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are crucial in predicting an element's reactivity and its ability to form chemical bonds.
In the case of calcium, its 2 valence electrons enable it to readily lose these electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, resulting in its tendency to form positive ions (Ca²âº).
7. Chemical Properties of Calcium
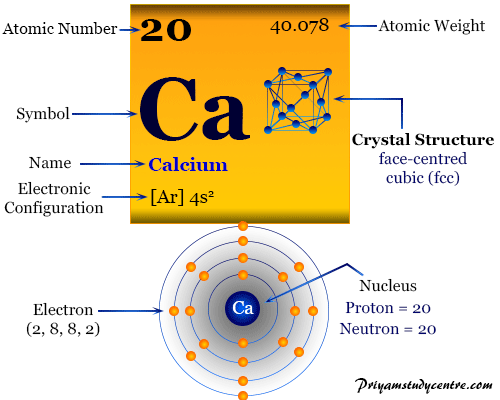
Chemical Properties of Calcium
Calcium's reactivity stems from its ability to lose 2 valence electrons, leading to the formation of Ca²âº ions.
This reactivity makes it an essential element in various biological processes, including muscle contraction and nerve signaling.
8. Applications of Calcium
Calcium finds applications beyond its biological significance.
It is widely used in construction materials, such as concrete, due to its ability to strengthen structures and improve durability.
9. Calcium and Health
Calcium is renowned for its role in maintaining strong bones and teeth. Adequate calcium intake is vital for bone health, and deficiencies can lead to conditions like osteoporosis.
Valence electrons in calcium are the key to understanding its chemical behavior and its interactions with other elements. With 2 valence electrons, calcium readily forms ions, contributing to its biological importance and various applications in everyday life. Whether it's the foundation of strong bones or its presence in construction materials, calcium's valence electrons play a crucial role in shaping its significance across different domains.