Valence Electrons of Chlorine: Unveiling the Outer Shell of an Elemental Titan
In the captivating realm of chemistry, the valence electrons of an element are like the keys to its intricate behavior. These electrons, residing in the outermost energy level or shell, orchestrate an element's interactions, bonding tendencies, and even its place on the periodic table. Among these fascinating elements, chlorine, with its atomic number 17 and symbol Cl, takes center stage. This article delves into the captivating world of chlorine's valence electrons, unraveling their significance, distribution, and impact on the element's chemical reactivity.
I. Introduction: The Dance of Electrons
At the heart of every chemical reaction lies the movement of electrons, and the valence electrons play a starring role in this grand performance. Valence electrons are the electrons found in the outermost shell of an atom. For chlorine, with an atomic structure of 2-8-7, the valence electrons are the seven electrons residing in the third shell.
The Dance of Electrons
II. Unveiling Chlorine's Valence Electrons
Chlorine's atomic structure, a mosaic of protons, neutrons, and electrons, gives rise to its unique properties. The third energy level of chlorine's electron cloud holds these seven valence electrons in a delicate balance. This configuration, 2-8-7, indicates that chlorine is just one electron short of achieving a stable, noble gas configuration similar to argon's 2-8-8.
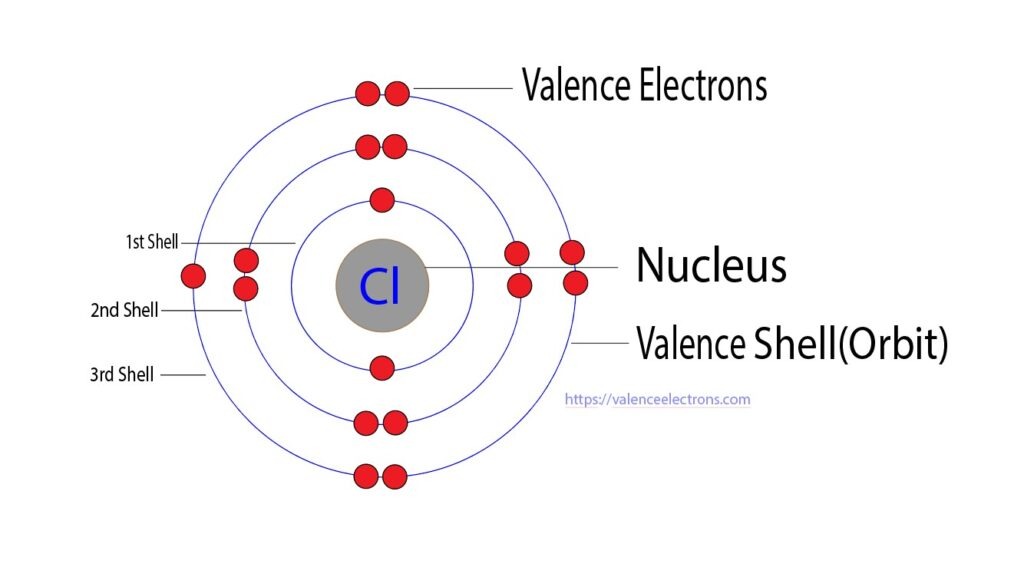
Chlorine's Valence Electrons
III. The Significance of a Full Octet
The quest for stability drives chemical reactions, and chlorine's valence electron count is pivotal in this quest. Like other elements, chlorine aims to achieve a full octet in its outermost shell. This octet rule, grounded in the noble gas configuration's stability, propels chlorine to engage in various chemical interactions, seeking to either gain an electron to complete its octet or shed one to reveal a stable duplet.
IV. Chemical Reactivity: Bonding Trends of Chlorine
Chlorine's valence electrons wield a mighty influence over its chemical behavior. With seven valence electrons, chlorine is one electron away from a full octet. This characteristic grants chlorine a strong tendency to engage in electron-hungry reactions, readily accepting an electron to achieve stability. This penchant for gaining an electron leads to its role as a highly reactive non-metal.
V. Formation of Ionic Compounds
Chlorine's craving for an additional electron makes it an excellent candidate for the formation of ionic compounds. It readily combines with elements willing to part with an electron, such as sodium. The electronegativity difference between chlorine and sodium fuels the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine, resulting in the creation of the iconic compound sodium chloride (NaCl), or common table salt.
VI. Covalent Bonds: Sharing is Caring
In addition to its ionic interactions, chlorine showcases its valence electrons' versatility through covalent bonding. When it pairs up with another non-metal, such as hydrogen, the sharing of electrons takes center stage. Hydrogen chloride (HCl), a colorless and pungent gas, exemplifies this dynamic through the shared electron pair that forms a covalent bond between the two atoms.
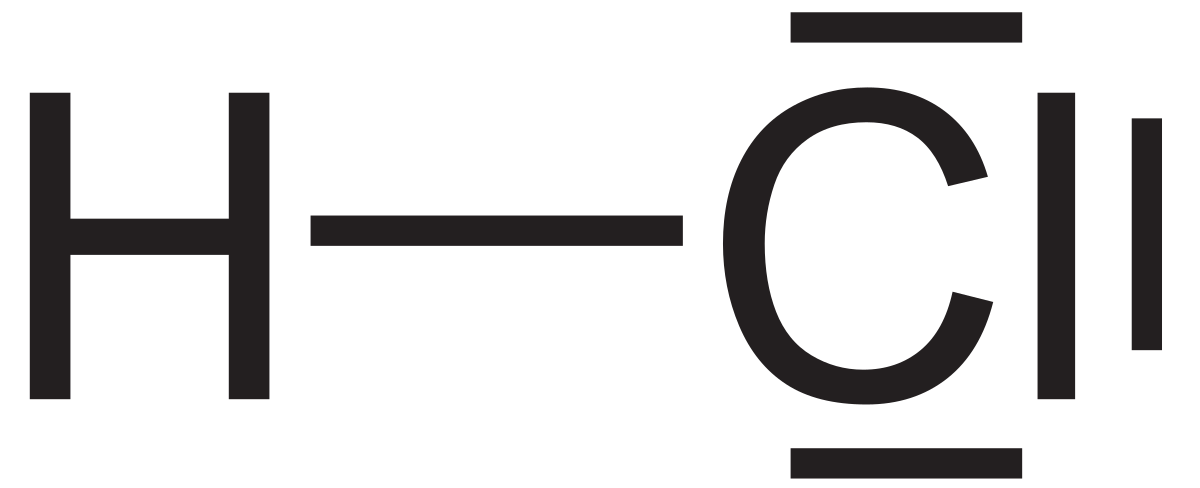
Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
VII. Applications and Beyond
Chlorine's valence electrons have far-reaching consequences in the world beyond the laboratory. The chemical reactivity of chlorine is harnessed in water treatment processes, where it eradicates harmful microorganisms. Its role extends to the production of plastics, pharmaceuticals, and even the realm of organic synthesis.
VIII. Conclusion: The Electrifying Influence of Valence Electrons
In the symphony of elements, chlorine's valence electrons compose a melodious tune of reactivity and interaction. The seven electrons dancing in its outermost shell guide chlorine's path, dictating its affinity for various bonding arrangements. From ionic compounds to covalent associations, chlorine's valence electrons govern its chemical destiny, making it an elemental titan with profound implications across industries and applications.