Which of These Are Part of a Basic Plot Structure? Select Three Options
Understanding the basic plot structure is essential for crafting engaging and coherent narratives. In this article, we will explore the fundamental elements that make up a basic plot structure. By identifying and analyzing these components, you'll gain insights into how stories are constructed and how they captivate readers. Let's delve into the key elements of a basic plot structure.
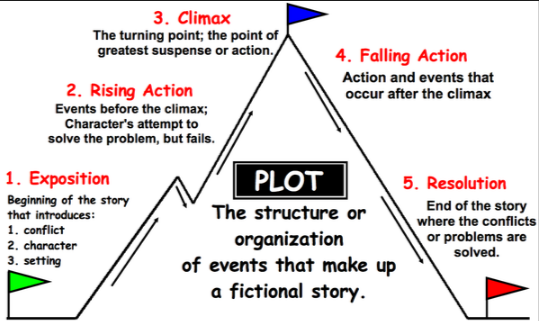
The structure or organization of events that make up a fictional story
I. Introduction to Basic Plot Structure:
Before we delve into the specific components of a basic plot structure, let's establish a clear understanding of what it entails.
II. The Components of a Basic Plot Structure:
A basic plot structure typically consists of several key elements that contribute to the development and progression of a story. Out of the following options, three are part of this structure:
1. Exposition: The exposition serves as the introduction to the story and sets the stage for the narrative. It establishes the main characters, their backgrounds, and the story's initial setting. Through exposition, readers gain essential information about the story's context and background.
2. Rising Action: The rising action refers to the series of events that build suspense, tension, and conflict in the story. It develops the plot and introduces obstacles or challenges that the protagonist must face. The rising action drives the narrative forward and keeps readers engaged as they anticipate the story's climax.
3. Climax: The climax is the highest point of tension or conflict in the story. It represents the turning point and the most significant moment of the narrative. During the climax, the protagonist confronts their central challenge, leading to a crucial decision or resolution. The climax is often emotionally charged and determines the outcome of the story.
4. Falling Action: The falling action follows the climax and showcases the consequences or aftermath of the protagonist's actions. It allows for the resolution of conflicts and ties up loose ends. Falling action provides closure and brings the story towards its conclusion.
5. Resolution: The resolution is the final part of the story where loose ends are tied up, and the narrative reaches its conclusion. It provides a sense of closure and may offer insights or lessons learned from the protagonist's journey. The resolution allows readers to reflect on the story's events and their implications.
6. Denouement: The denouement, also known as the conclusion, occurs after the resolution and provides additional closure or final thoughts. It allows for reflection on the story's events and their impact on the characters and the world they inhabit. The denouement wraps up any remaining loose ends and leaves readers with a sense of completion.
III. The Importance of a Basic Plot Structure:
Understanding and utilizing a basic plot structure is crucial for creating compelling narratives. By incorporating the key elements mentioned above, writers can craft stories that engage readers, build suspense, and deliver satisfying resolutions. A well-structured plot keeps readers invested in the story and allows them to connect with the characters and their journey.
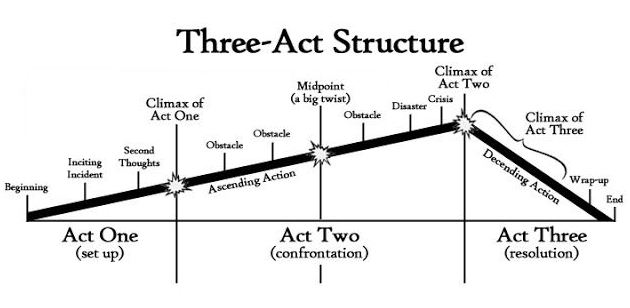
Three-act Structure
A basic plot structure serves as the framework for storytelling, providing a roadmap for crafting engaging narratives. By incorporating elements such as exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution, and denouement, writers can create cohesive and compelling stories that resonate with readers. Understanding the components of a basic plot structure empowers writers to captivate audiences and take them on memorable literary journeys.