Orbital Diagram of Boron: Understanding the Electronic Configuration
In the world of chemistry, understanding the electronic configuration of elements is essential for comprehending their properties and behaviors. Boron, with its atomic number 5, has a unique orbital diagram that determines its chemical characteristics. In this article, we will delve into the orbital diagram of boron and explore its electronic configuration in detail.

Orbital diagram of boron
1. The Atomic Structure of Boron:
Before we dive into the orbital diagram, let's briefly discuss the atomic structure of boron. Boron has an atomic number of 5, indicating that it has five protons and five electrons. Its atomic symbol is B, and it belongs to Group 13 (formerly known as Group IIIA) of the periodic table.
2. Orbital Diagram Basics:
To understand the orbital diagram of boron, we need to be familiar with the basics of orbital notation. Orbitals are regions of space around the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. They are denoted by letters (s, p, d, f) and assigned to specific energy levels (1, 2, 3, etc.).
3. The Electronic Configuration of Boron:
The electronic configuration of boron is 1s² 2s² 2p¹. Let's break it down further:
-
1s²: This represents the 1s orbital, which can accommodate a maximum of two electrons. In boron, both slots in the 1s orbital are filled.
-
-
2s²: The 2s orbital can also accommodate a maximum of two electrons. In boron, both slots in the 2s orbital are filled.
-
-
2p¹: The 2p orbital has three sub-orbitals (2px, 2py, 2pz), each capable of holding two electrons. In boron, only one electron occupies the 2p orbital, specifically in the 2px sub-orbital.
-
4. Orbital Diagram of Boron:
Now, let's represent the electronic configuration of boron in an orbital diagram. The diagram consists of boxes to represent orbitals and arrows to represent electrons. Here's how it looks:
1s ↑↓ 2s ↑↓ 2p ↑
Note that the 1s and 2s orbitals are completely filled with electrons (↑↓), while the 2p orbital has one unpaired electron (↑).
5. Significance of the Orbital Diagram:
The orbital diagram of boron helps us understand its chemical behavior. Since boron has an unpaired electron in the 2p orbital, it is more likely to participate in chemical reactions and bonding. This unpaired electron makes boron highly reactive and forms compounds with various elements.
6. Properties and Applications of Boron:
Boron exhibits unique properties due to its electronic configuration. It is a metalloid with both metallic and non-metallic characteristics. Boron compounds, such as borates and boron nitride, have applications in various industries, including agriculture, electronics, and materials science.
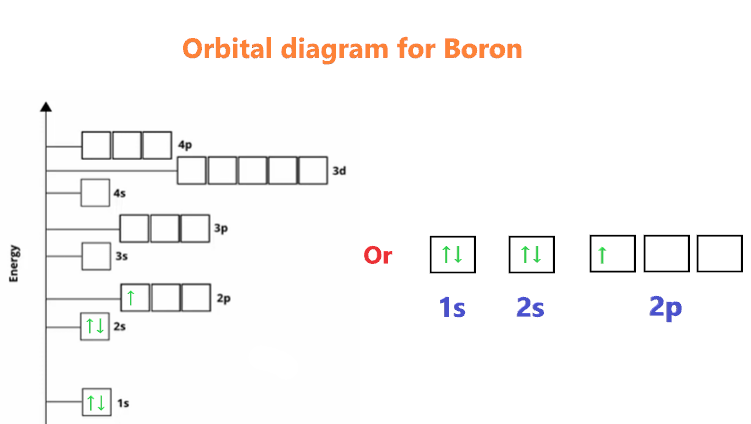
Orbital diagram of boron
Understanding the orbital diagram of boron is crucial for comprehending its electronic configuration and chemical behavior. The electronic configuration of boron, represented by the 1s² 2s² 2p¹ configuration, reveals an unpaired electron in the 2p orbital, making boron highly reactive. By studying the orbital diagram, scientists and chemists can gain insights into the properties and applications of this fascinating element.