The Opposite of Gray on the Color Wheel: Exploring Complementary Colors
In the world of color theory, understanding complementary colors can help us create visually appealing and harmonious color schemes. In this article, we will delve into the concept of complementary colors and explore what color lies opposite to gray on the color wheel. Join us as we unravel the relationship between gray and its complementary color.
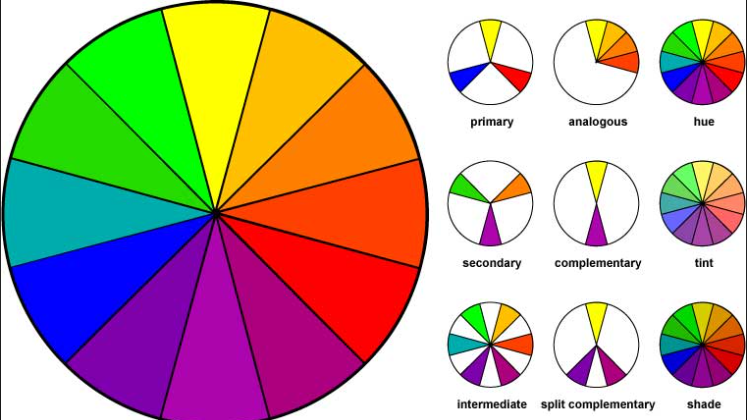
Color wheel
I. Understanding Gray:
Before we explore the opposite of gray on the color wheel, let's familiarize ourselves with the characteristics and symbolism of the color gray.
A. Definition:
- Gray is a neutral color that is often associated with balance, neutrality, and sophistication.
- It is created by mixing black and white, resulting in various shades of gray.
B. Symbolism:
- Gray is often associated with practicality, stability, and maturity.
- It is a versatile color that can evoke feelings of calmness and serenity.
II. The Color Wheel and Complementary Colors:
The color wheel is a visual representation of the relationships between colors. Understanding the concept of complementary colors is essential in color theory.
A. Definition:
- Complementary colors are pairs of colors that are located opposite each other on the color wheel.
- When placed together, they create a strong contrast and enhance each other's vibrancy.
B. Use in Design:
- Designers often utilize complementary colors to create visually appealing and balanced compositions.
- Complementary colors can be employed in various design fields, including graphic design, interior design, and fashion.
III. The Opposite of Gray on the Color Wheel:
Determining the exact opposite of gray on the color wheel requires considering the specific shade of gray.
A. Gray as a Neutral: As gray is a neutral color, its opposite on the color wheel can vary based on the underlying undertones.
B. Complementary Colors for Neutral Grays:
- For neutral grays, which have no strong warm or cool undertones, their complementary colors lie on the opposite side of the color wheel.
- In general, warm grays tend to have cooler complements, while cool grays have warmer complements.
C. Warm Gray:
- If the gray has warm undertones, its complementary color will be a cool color.
- Examples of complementary colors for warm grays include shades of blue or green.
D. Cool Gray:
- Cool grays, on the other hand, have warm complements.
- Complementary colors for cool grays can include warmer hues like yellow or orange.
IV. Creating Harmonious Color Schemes:
Understanding the complementary color to gray opens up possibilities for creating harmonious color schemes.
A. Using Complementary Colors:
- Pairing gray with its complementary color can create a striking contrast and visual interest.
- For warm grays, consider incorporating cool tones as complements, while cool grays can be paired with warmer hues.
B. Exploring Analogous Colors:
- Analogous colors, which are adjacent to each other on the color wheel, can also be combined with gray for a harmonious color scheme.
- Analogous colors can create a sense of unity and cohesion.
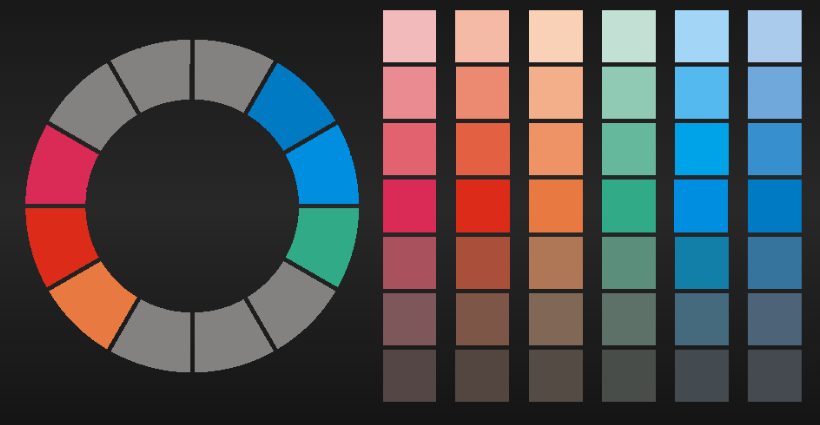
Heather Durnin Gr.8 Classroom wiki
While the opposite of gray on the color wheel can vary based on the specific shade and undertones, understanding the concept of complementary colors allows us to create visually pleasing color schemes. Gray, as a neutral color, can be complemented by a range of cool or warm hues depending on its undertones. By exploring complementary colors and considering analogous color schemes, designers and enthusiasts can elevate their understanding of color relationships and create visually captivating compositions. So, the next time you work with gray, consider its complementary color and experiment with different combinations to achieve captivating and harmonious designs.