What Problems Does a Tortuous Colon Cause?
A tortuous colon, also known as a redundant colon or elongated colon, refers to a condition where the large intestine has excessive loops or twists. While it doesn't necessarily cause serious health complications, it can lead to certain problems and discomfort. This article aims to explore the various issues associated with a tortuous colon and their potential impact on individuals.
1. Understanding a Tortuous Colon:
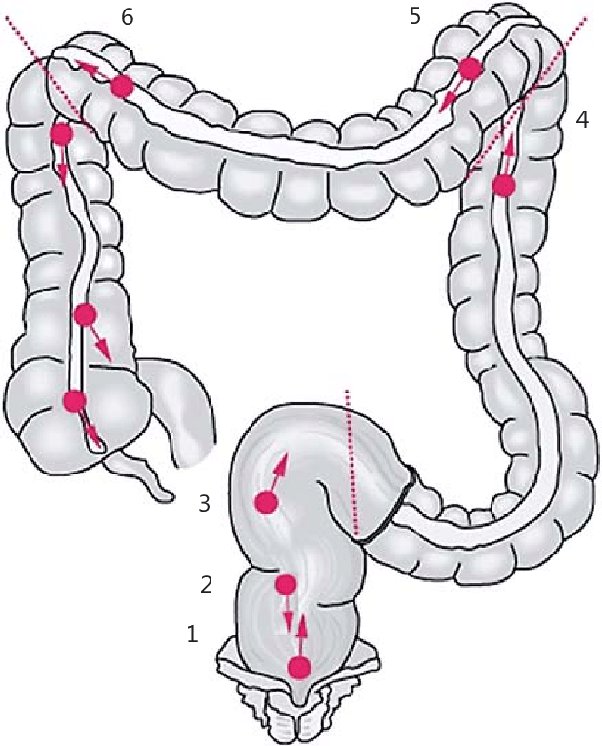
Understanding a Tortuous Colon
1.1 Definition: A tortuous colon is characterized by excessive twisting or looping of the large intestine.
1.2 Causes: The condition can be congenital or acquired due to factors like age, chronic constipation, or certain medical conditions.
1.3 Diagnosis: Medical professionals employ diagnostic tests such as X-rays, colonoscopies, or barium enemas to identify a tortuous colon.
2. Symptoms and Discomfort:
Symptoms and Discomfort
2.1 Abdominal Pain: Individuals with a tortuous colon may experience intermittent or persistent abdominal pain, often in the lower left quadrant.
2.2 Bowel Movement Changes: The condition can cause irregular bowel movements, including constipation or diarrhea.
2.3 Bloating and Gas: Many individuals with a tortuous colon report increased bloating, gas, and discomfort.
2.4 Nausea and Vomiting: In severe cases, the twisting of the colon may lead to nausea and vomiting.
3. Complications of a Tortuous Colon:
3.1 Intestinal Obstruction: Twists and loops in the colon can result in partial or complete obstruction, leading to severe pain and bowel movement difficulties.
3.2 Diverticulosis: A tortuous colon can increase the risk of diverticulosis, where small pouches form along the colon's wall, potentially causing inflammation or infection.
3.3 Increased Risk of Colon Volvulus: The twisted nature of a tortuous colon may predispose individuals to colon volvulus, a condition characterized by the twisting of the intestine on itself, leading to reduced blood flow and potential tissue damage.
4. Treatment Options:
4.1 Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity can help alleviate symptoms and promote regular bowel movements.
4.2 Medications: Depending on the symptoms, doctors may prescribe medications to manage pain, bloating, or regulate bowel movements.
4.3 Surgical Intervention: In rare cases where complications arise or symptoms persist, surgical procedures such as colectomy or colon resection may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the colon.
5. Coping with a Tortuous Colon:
5.1 Dietary Recommendations: Including fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can aid in maintaining bowel regularity.
5.2 Hydration: Drinking an adequate amount of water can prevent dehydration and soften the stool, easing bowel movements.
5.3 Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity promotes overall colon health and helps prevent constipation.
5.4 Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so adopting stress-reduction techniques like meditation or counseling can be beneficial.
A tortuous colon may cause several problems and discomfort, including abdominal pain, irregular bowel movements, bloating, and gas. While complications such as intestinal obstruction or diverticulosis are possible, most cases can be managed through lifestyle modifications and medications. Surgical intervention is reserved for severe cases. By understanding the symptoms, seeking medical advice, and adopting healthy habits, individuals with a tortuous colon can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life.