What Does Gravity Do to Cause Rain to Happen?
Rain is a natural phenomenon that sustains life on Earth. Have you ever wondered why raindrops fall from the sky? The answer lies in the interaction between gravity and the water cycle. In this article, we will explore the role of gravity in causing rain to happen, analyzing each step of the process in detail.
Gravity in the Water Cycle Science
1. The Water Cycle: A Brief Overview
Before diving into the connection between gravity and rain, let's first understand the water cycle. The water cycle is a continuous process where water evaporates from the Earth's surface, condenses in the atmosphere to form clouds, and then returns to the surface as precipitation, including rain.
2. Evaporation: The Beginning of the Journey
The water cycle begins with the process of evaporation. Solar energy heats the Earth's surface, causing water in oceans, lakes, and rivers to turn into water vapor. This water vapor rises into the atmosphere due to its lower density compared to the surrounding air.
3. Condensation: Creating Clouds
As the water vapor rises higher into the atmosphere, the air temperature drops, causing the water vapor to cool and condense into tiny water droplets. These droplets gather around particles in the atmosphere, forming clouds.
4. The Role of Gravity in Clouds
Gravity plays a crucial role in the formation and movement of clouds. Clouds consist of water droplets and ice crystals that are suspended in the air. Although these particles are tiny, they have mass, which means gravity exerts a force on them. However, other factors, such as air currents and updrafts, also influence the shape and movement of clouds.
5. Precipitation: The Release of Water
When clouds become saturated with water droplets and the updrafts can no longer support their weight, gravity takes over. Water droplets begin to merge and grow larger, eventually becoming heavy enough to fall as precipitation.
6. Rainfall: Gravity's Final Act
Rainfall occurs when the water droplets in the clouds become too large to stay aloft and succumb to the pull of gravity. These raindrops fall towards the Earth's surface under the force of gravity, providing the much-needed water to sustain ecosystems, agriculture, and our daily lives.
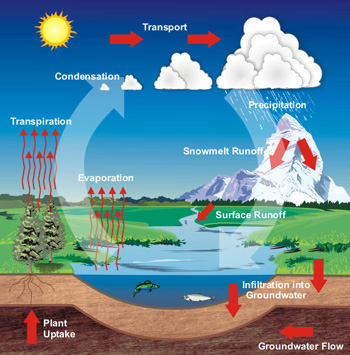
The Water cycle
7. Factors Affecting Rainfall Amounts
The amount of rainfall in a particular area is influenced by various factors. These include:
-
Humidity: Higher humidity levels contribute to the formation of more water vapor, potentially leading to increased rainfall.
-
-
Topography: Mountains and hills can affect rainfall patterns as moist air is forced to rise, cool, and condense, resulting in more precipitation on windward slopes.
-
-
Air Masses: The collision of warm and cold air masses can trigger the lifting of air, leading to cloud formation and subsequent rainfall.
-
-
Climate Change: Alterations in global climate patterns can affect rainfall distribution and intensity, causing extreme weather events.
8. Rain's Impact on the Environment
Rain is vital for the Earth's ecosystems and plays a crucial role in nourishing plant life and replenishing freshwater sources. Additionally, rain helps maintain temperature balance and cleanses the atmosphere by removing pollutants.
9. The Human Factor: Rain and Us
Rain has a significant impact on human activities and daily life. From agriculture and water supply to recreational activities, understanding the role of gravity in causing rain can help us better prepare for and adapt to different weather conditions.
In conclusion, gravity is the driving force behind the occurrence of rain. As water evaporates, condenses, and forms clouds, gravity continues to shape and influence these clouds until precipitation occurs. Understanding the relationship between gravity and rain is essential for comprehending the water cycle and the significant role rain plays in sustaining life on Earth.