Identify Three Situations in Which Convection Occurs
Convection is a process of heat transfer that occurs in fluids (liquids or gases) when there is a difference in temperature within the fluid. It plays a crucial role in various natural and artificial phenomena. This article aims to explore and identify three situations in which convection occurs. By understanding these situations, we can gain insights into the significance of convection in different contexts.
1. Atmospheric Convection:
One of the most prominent examples of convection occurs in the Earth's atmosphere.
Atmospheric convection is responsible for weather patterns, cloud formation, and global climate systems.
It involves the movement of warm air rising and cooler air sinking. When the Sun heats the Earth's surface, the air in contact with it becomes warm and less dense, causing it to rise.
As the warm air rises, it cools, leading to the condensation of water vapor and the formation of clouds. Eventually, this convection process results in precipitation, such as rain or snow.
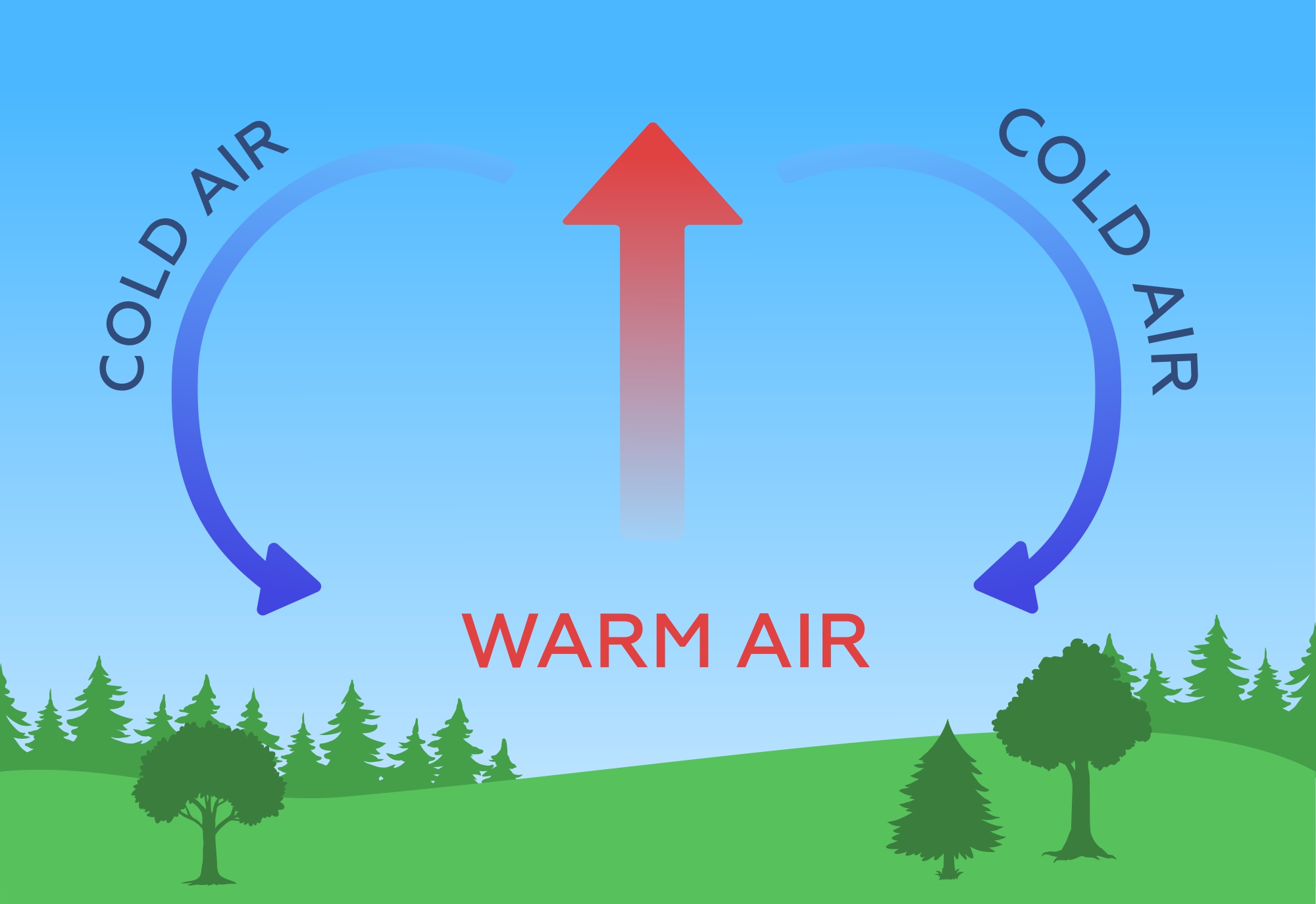
Atmospheric Convection
2. Oceanic Convection:
Convection also plays a crucial role in oceanic processes.
Oceanic convection occurs when there are temperature and salinity differences within the water column.
This phenomenon is particularly notable in regions where warm and cold currents meet, such as the Gulf Stream in the Atlantic Ocean.
The warm water from the Gulf Stream moves toward colder regions, releasing heat and moisture into the atmosphere, which influences weather patterns in nearby coastal areas.
Oceanic convection affects the distribution of heat and nutrients, impacting marine ecosystems and the global climate.
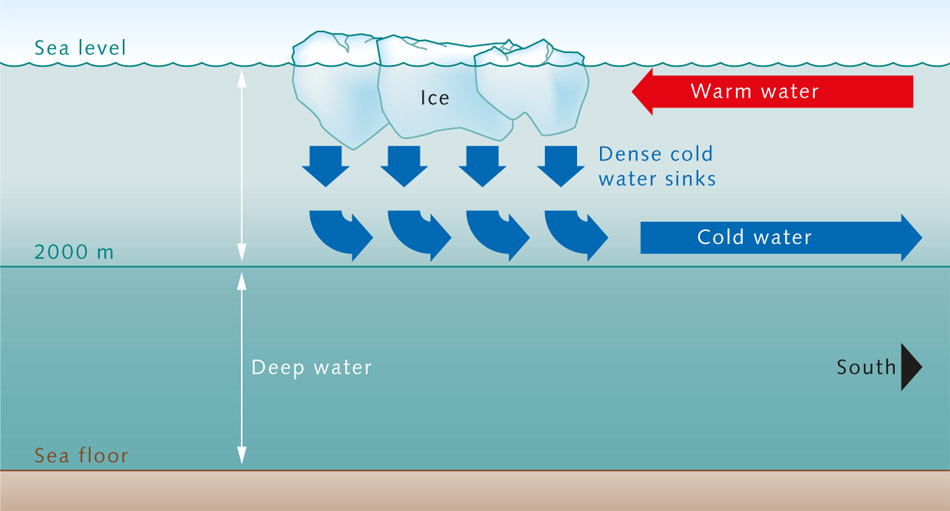
Oceanic Convection
3. Convection in Engineering:
Convection is extensively utilized in engineering applications to transfer heat efficiently.
One notable situation where convection occurs is in heating and cooling systems.
For example, in a forced-air heating system, warm air is generated by a furnace and then circulated through ducts to different parts of a building.
The warm air rises due to convection, distributing heat throughout the space.
Similarly, cooling systems, such as air conditioners, use convection to remove heat from indoor environments.
In this case, cool air displaces warm air, creating a comfortable living or working environment.
Convection is a fundamental process that occurs in various contexts, ranging from atmospheric phenomena to engineering applications. Identifying three situations where convection occurs highlights its significance in different fields. Understanding atmospheric convection helps us comprehend weather patterns and climate systems. Oceanic convection plays a vital role in the distribution of heat and nutrients in oceans, impacting marine life and global climate. Furthermore, convection is leveraged in engineering applications, such as heating and cooling systems, to efficiently transfer heat. By recognizing these situations, we can appreciate the importance of convection and its impact on our daily lives and the environment.