Telnet, SSH, and VNC: Understanding the Different Types of Software
In the realm of computer networking and remote access, Telnet, SSH, and VNC are three commonly used protocols or technologies. They play a crucial role in facilitating secure and efficient communication between computers over networks. This article aims to explore and differentiate these three types of software, shedding light on their features, functionalities, and areas of application.
1. Telnet: The Original Remote Access Protocol
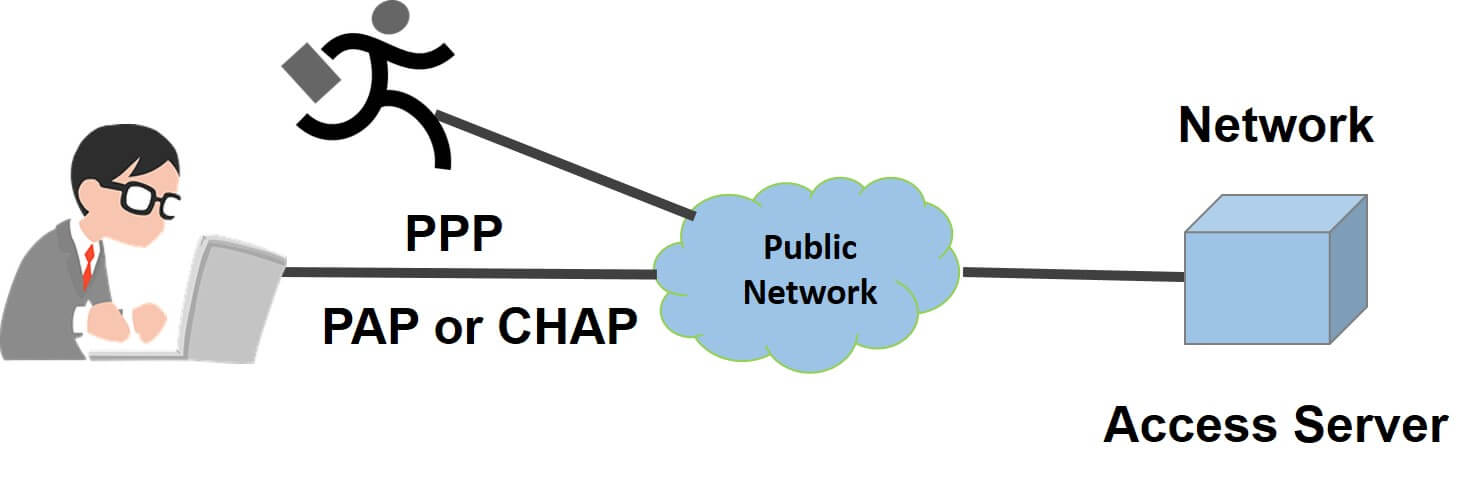
The Original Remote Access Protocol
Telnet, short for "telecommunication network," is a network protocol that enables remote access to computers or networking devices. It allows users to establish a text-based communication session with a remote system over a TCP/IP network.
Telnet sessions operate on port 23, and the protocol provides a virtual terminal interface for interacting with the remote device's command-line interface.
Despite being widely used in the past, Telnet has become less popular due to security vulnerabilities.
Telnet transmits data, including usernames, passwords, and commands, in plaintext, making it susceptible to interception and unauthorized access. Therefore, it is recommended to use more secure alternatives like SSH or VNC.
2. SSH: Secure and Encrypted Remote Access
Secure and Encrypted Remote Access
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol designed to provide secure remote access to computers and perform secure file transfers. SSH was developed as a secure alternative to Telnet, addressing the security concerns associated with plaintext transmission.
The primary advantage of SSH lies in its ability to encrypt data transmission, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. SSH employs encryption algorithms to secure the connection, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to eavesdrop on the communication.
Additionally, SSH provides authentication mechanisms, such as password-based or key-based authentication, to verify the identity of the connecting parties.
SSH is widely used in various scenarios, including remote administration, remote command execution, and secure file transfers. Its popularity stems from its robust security measures and its compatibility with multiple operating systems and devices.
3. VNC: Remote Desktop Sharing and Control
VNC, or Virtual Network Computing, is a graphical desktop sharing system that allows users to remotely access and control another computer's desktop environment.
Unlike Telnet and SSH, which are primarily text-based, VNC provides a graphical interface, enabling users to interact with the remote system as if they were physically present in front of it.
VNC operates using a client-server architecture. The VNC server, installed on the remote system, transmits graphical screen updates to the VNC client running on the local machine.
This allows users to view and control the remote desktop, facilitating collaborative work, remote technical support, or accessing a computer located in a different physical location.
VNC offers various features, such as file transfer capabilities, remote printing, and multiple client connections. It supports different operating systems and can be utilized across a range of devices, including desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
Telnet, SSH, and VNC are three distinct types of software used in the domain of computer networking and remote access. While Telnet was once widely used but is now considered less secure, SSH has emerged as the preferred choice due to its encryption and authentication features. VNC, on the other hand, provides graphical desktop sharing, allowing users to remotely control another computer's desktop environment.
Understanding the differences between these three software types is crucial for network administrators, IT professionals, and anyone involved in remote access or administration tasks. By choosing the appropriate software based on the specific requirements and security considerations, users can ensure efficient and secure remote communication and control.