Which Electromagnetic Wave Transfers the Least Amount of Energy: Gamma, X-Ray, Ultraviolet, or Microwave?
Electromagnetic waves are a fundamental aspect of physics and play a crucial role in various applications and fields. In this article, we explore the characteristics and energy transfer capabilities of different electromagnetic waves, specifically focusing on gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet waves, and microwaves. Join us as we examine these waves and determine which one transfers the least amount of energy.

The electromagnetic spectrum
1. Understanding Electromagnetic Waves:
- Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves: Providing a brief overview of electromagnetic waves, their properties, and their classification based on wavelength and frequency.
- Energy Transfer in Electromagnetic Waves: Explaining how electromagnetic waves transfer energy and the relationship between energy and wavelength.
2. Gamma Rays:
- Characteristics of Gamma Rays: Describing the properties and characteristics of gamma rays, including their high frequency and short wavelength.
- Energy Transfer in Gamma Rays: Exploring the energy transfer capabilities of gamma rays and their interaction with matter.
3. X-Rays:
- Properties of X-Rays: Discussing the properties and uses of X-rays, including their ability to penetrate matter and produce detailed images.
- Energy Transfer in X-Rays: Examining the energy transfer characteristics of X-rays and their impact on biological tissues.
4. Ultraviolet Waves:
- Ultraviolet Spectrum: Exploring the different regions of the ultraviolet spectrum and their varying energy levels.
- Energy Transfer in Ultraviolet Waves: Analyzing the energy transfer capabilities of ultraviolet waves and their effects on materials and living organisms.
5. Microwaves:
- Microwave Characteristics: Describing the properties and uses of microwaves, including their longer wavelengths and lower frequencies.
- Energy Transfer in Microwaves: Investigating the energy transfer capabilities of microwaves and their role in heating food and communication technologies.
6. Comparing Energy Transfer:
- Energy Levels and Rankings: Comparing the energy levels of gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet waves, and microwaves to determine which transfers the least amount of energy.
- Factors Affecting Energy Transfer: Discussing other factors that influence energy transfer, such as intensity, exposure time, and the interaction with matter.
7. Practical Applications and Safety Considerations:
- Medical Applications: Highlighting the use of gamma rays and X-rays in medical imaging and treatments, and the protective measures in place to ensure safety.
- Technological Applications: Discussing the utilization of microwaves in various technologies, such as cooking appliances and telecommunications.
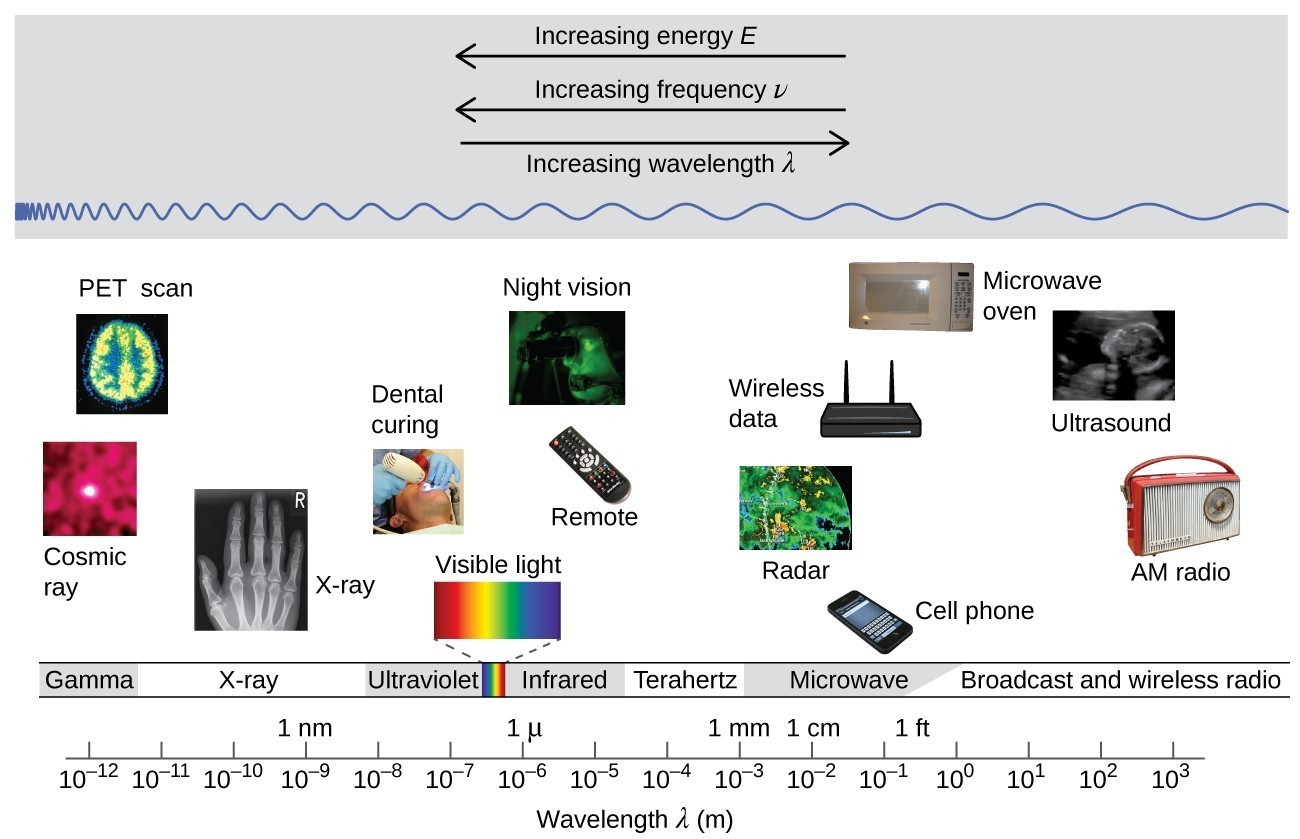
Electromagnetic wave
In conclusion, when comparing gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet waves, and microwaves, it can be determined that microwaves transfer the least amount of energy. With their longer wavelengths and lower frequencies, microwaves have lower energy levels compared to gamma rays, X-rays, and ultraviolet waves. Understanding the energy transfer capabilities of different electromagnetic waves is crucial for various scientific, medical, and technological applications. By comprehending these distinctions, we can harness the potential of electromagnetic waves while ensuring safety and optimizing efficiency in their usage.