Exploring the Best Examples of How Electromagnetic Energy Powers Everyday Life
Electromagnetic energy is a fundamental force that surrounds us and plays a vital role in our daily lives. From the moment we wake up in the morning to the time we go to bed at night, we encounter numerous instances where electromagnetic energy is utilized to power and enable various technologies and activities. In this article, we will delve into some of the best examples of how electromagnetic energy is harnessed and applied in everyday life, highlighting the incredible impact it has on our modern world.
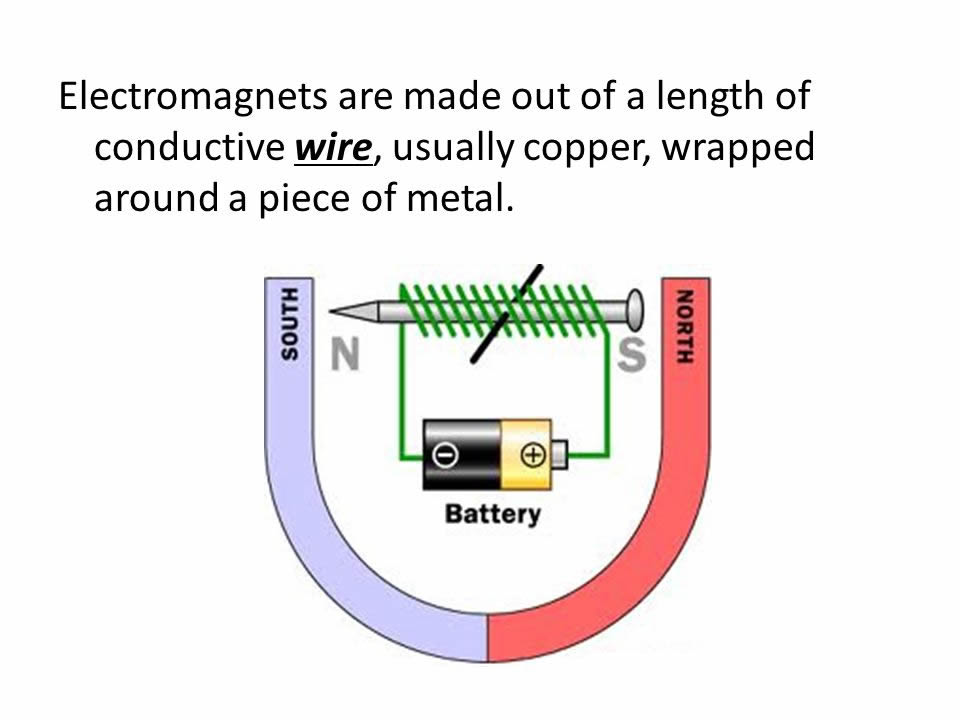
What is the Electromagnets
1. Electromagnetic Energy in Communication Systems
- Cell Phones: The ubiquitous devices we rely on for communication utilize electromagnetic energy in the form of radio waves to transmit and receive signals.
- Wi-Fi: Wireless internet connectivity relies on electromagnetic energy to transmit data through radio waves, enabling seamless online experiences.
- Television and Radio Broadcasting: These forms of media rely on electromagnetic waves to transmit audio and video signals to our homes, bringing entertainment and information right to our screens and speakers.
2. Electromagnetic Energy in Transportation
- Electric Vehicles: The rise of electric cars is fueled by electromagnetic energy, as it powers the electric motors that propel these vehicles, offering a greener alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) Trains: These futuristic trains use powerful electromagnetic fields to levitate and propel the train cars, allowing for high-speed transportation with minimal friction.
3. Electromagnetic Energy in Medical Applications
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This non-invasive medical imaging technique uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of internal body structures, aiding in diagnosis and treatment.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): ECG devices measure the electrical activity of the heart, helping healthcare professionals detect and diagnose heart conditions.
- Radiation Therapy: Electromagnetic energy in the form of high-energy X-rays or gamma rays is used in cancer treatment to destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
4. Electromagnetic Energy in Power Generation and Distribution
- Hydroelectric Power Plants: The movement of water generates electromagnetic energy, which is then converted into electrical energy to power homes and industries.
- Solar Panels: Photovoltaic cells in solar panels convert sunlight, which is a form of electromagnetic energy, into electricity, providing a clean and sustainable source of power.
5. Electromagnetic Energy in Household Appliances and Electronics
- Microwave Ovens: These kitchen appliances utilize electromagnetic energy in the form of microwaves to heat and cook food quickly and efficiently.
- Light Bulbs: Incandescent, fluorescent, and LED light bulbs emit light by harnessing electromagnetic energy, providing illumination for our homes and workplaces.
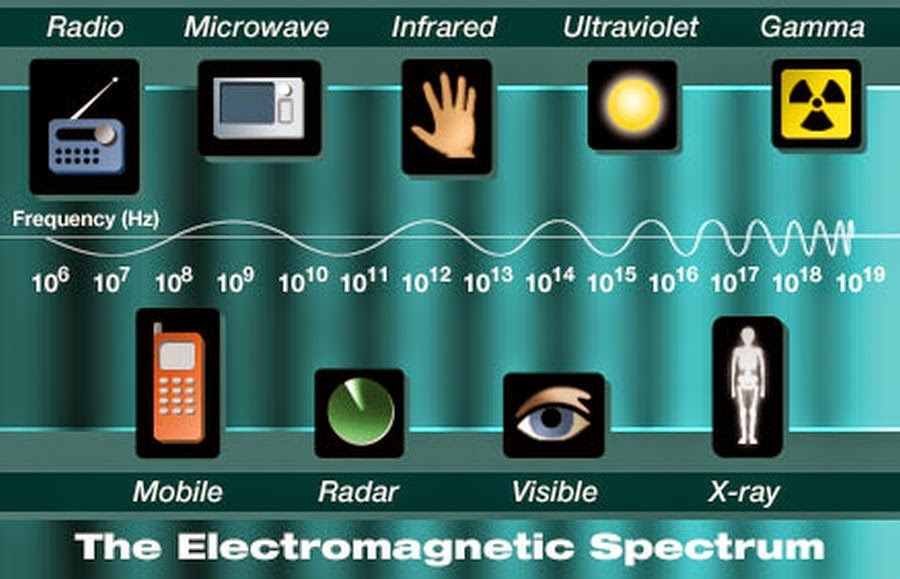
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
In conclusion, electromagnetic energy is a driving force behind numerous technologies and activities that shape our everyday lives. From communication systems and transportation to medical applications and power generation, the examples discussed in this article highlight the diverse and impactful uses of electromagnetic energy. As we continue to advance technologically, our reliance on electromagnetic energy will only grow, ushering in new innovations and improving our quality of life. By understanding and appreciating the role of electromagnetic energy, we can better grasp the wonders of the modern world and the incredible possibilities it offers.