Understanding the Link between the Law of Demand and Excess Demand
The law of demand and excess demand are fundamental concepts in economics that help explain the dynamics of supply and demand in a market. This article aims to explore the connection between these two concepts and shed light on how they shape market behavior. By understanding the relationship between the law of demand and excess demand, we can gain insights into pricing, market equilibrium, and the factors that influence consumer behavior.
1. The Law of Demand:
The law of demand states that, ceteris paribus, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded by consumers decreases, and vice versa. This inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded is based on the assumption that other factors remain constant, such as income, consumer preferences, and the prices of related goods.
Understanding the law of demand is crucial for comprehending how changes in price affect consumer behavior. When prices rise, consumers typically seek alternatives or reduce their consumption, leading to a decrease in demand. Conversely, when prices decrease, consumers tend to increase their purchases, resulting in an upward shift in demand.
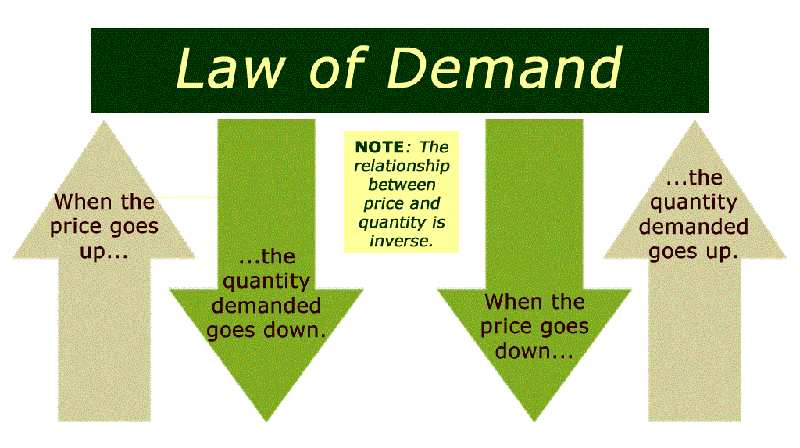
The Law of Demand
2. Excess Demand:
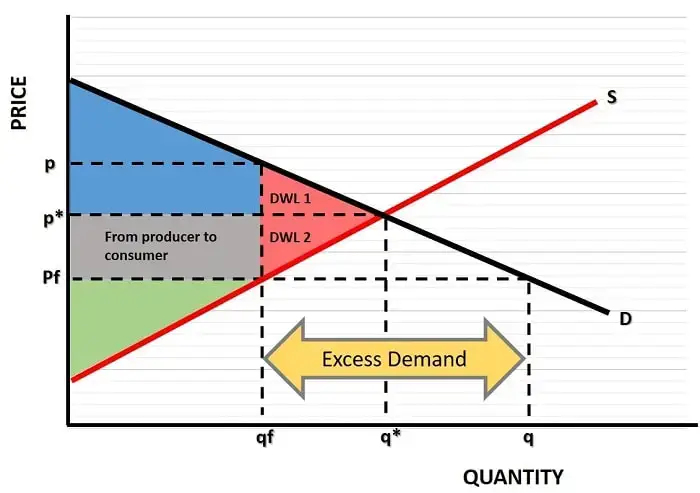
Excess demand, also known as a shortage, occurs when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied at a given price. This situation arises when the market price is set below the equilibrium price, creating an imbalance between supply and demand.
Excess demand indicates that consumers are willing to buy more of a product than is currently available in the market. This condition can lead to various consequences, such as price increases, rationing, and a competitive bidding environment. Suppliers may respond by raising prices to align with demand or by increasing production to meet the excess demand.
Excess Demand
3. The Relationship between the Law of Demand and Excess Demand:
The law of demand and excess demand are closely interconnected. The law of demand explains the consumer behavior aspect, stating that as prices decrease, quantity demanded increases. When prices fall below the equilibrium level, demand surpasses supply, resulting in excess demand.
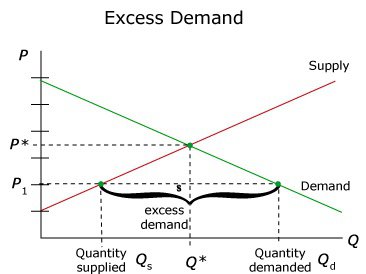
Law of demand and excess demand
Excess demand acts as a mechanism to restore equilibrium in the market. When a shortage occurs, prices tend to rise, thereby reducing demand and encouraging suppliers to produce more. This adjustment process continues until the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied, reaching a state of market equilibrium.
Understanding the relationship between the law of demand and excess demand is vital for policymakers, businesses, and economists. It enables them to anticipate and respond to market imbalances and fluctuations. By considering factors such as elasticity of demand, production capacity, and market trends, stakeholders can make informed decisions to address excess demand situations effectively.
The law of demand and excess demand are essential concepts in economics that help us understand the dynamics of supply and demand in a market. The law of demand explains the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, while excess demand occurs when quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied at a given price.
Recognizing the connection between these concepts allows us to analyze market behavior, predict price movements, and identify potential shortages or surpluses. By understanding how excess demand arises from the law of demand, policymakers, businesses, and economists can take appropriate measures to restore market equilibrium.
As markets evolve and consumer preferences change, the interplay between the law of demand and excess demand remains a crucial area of study. Continued research and analysis will enhance our understanding of these concepts, leading to more effective decision-making and improved economic outcomes.