Exploring Planetary Orbits: Unveiling the Least Circular Path
The celestial dance of planets around the sun has captivated humanity for centuries. Each planet follows a unique path in its orbit, some resembling perfect circles while others exhibit more elliptical shapes. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of planetary orbits and discover which planet's path deviates the most from a circular shape. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of celestial mechanics.
NASA has discovered 7 Earth-linke planets orbiting a star just 40 light
1. Understanding Planetary Orbits: The Solar System's Harmony
Before we delve into the intricacies of non-circular orbits, let's gain a basic understanding of planetary motion.
The planets in our solar system revolve around the sun in elliptical paths known as orbits.
These orbits are governed by gravitational forces and various factors that influence their shapes.
2. The Eccentricity Factor: Measuring Orbital Deviation
Eccentricity is a fundamental parameter used to quantify the shape of an orbit. It determines how elliptical or circular an orbit appears. An eccentricity of 0 represents a perfectly circular orbit, while values closer to 1 indicate more elongated or elliptical paths.
3. Unveiling the Least Circular Orbit: The Answer Revealed
Among the planets in our solar system, the planet with the least circular orbit is Mercury.
Mercury's orbit has an eccentricity of approximately 0.2056, making it the planet with the highest deviation from a perfect circle.
Its elliptical path brings it closer to the sun during perihelion (closest approach) and takes it farther during aphelion (farthest point).
4. Factors Influencing Orbital Eccentricity
Several factors contribute to the eccentricity of a planet's orbit:
- Gravitational Influences: Interactions with other celestial bodies, such as planets or moons, can perturb a planet's orbit and increase its eccentricity.
- Tidal Forces: The gravitational pull from other bodies, like the moon, can also affect a planet's orbit and introduce deviations from circularity.
- Planetary Resonances: The gravitational interactions between planets can create resonances that cause slight perturbations in their orbits.
5. The Impact of Eccentric Orbits
While Mercury's orbit stands out as the least circular, it is important to note that eccentricity alone does not determine a planet's significance or characteristics. The eccentricity of an orbit does not directly correlate with a planet's size, atmosphere, or other properties.
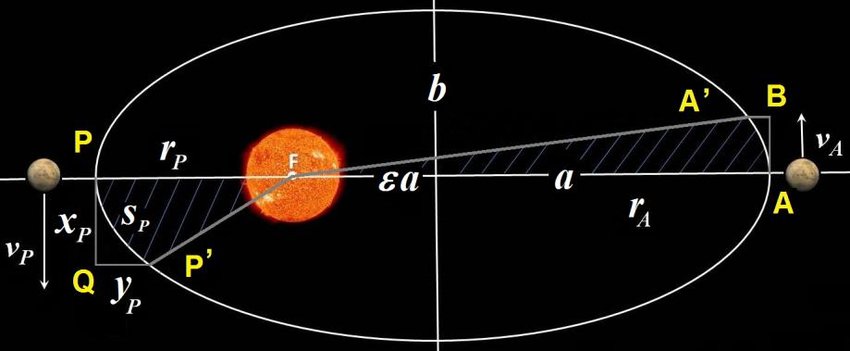
The elliptical orbit of a planet
The captivating world of planetary orbits unveils the diversity and complexity of our solar system. Among the planets, Mercury's elliptical path stands out as the least circular orbit, deviating significantly from a perfect circle. As we continue to explore and study the mysteries of celestial mechanics, we gain deeper insights into the forces shaping our cosmic neighborhood. Whether circular or eccentric, each planet's orbit offers unique glimpses into the grand tapestry of the universe.