Unveiling the Mystery: Which of These Will Reflect Light with the Highest Frequency?
Light, an essential component of our world, encompasses a spectrum of frequencies. The question of which material reflects light with the highest frequency captivates both scientists and curious minds alike. In this article, we embark on a journey to explore this enigma, delving into the principles of light reflection and investigating various materials that exhibit remarkable reflective properties. By understanding the relationship between frequency and reflection, we aim to shed light on the intriguing choices and unveil the substance that holds the key to reflecting light with the highest frequency.
1. Understanding Light Frequency
Before we dive into the materials that reflect light with the highest frequency, it's crucial to comprehend the concept of light frequency. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that propagates as waves, and its frequency refers to the number of wave cycles per unit of time. The frequency determines the color of light, with higher frequencies corresponding to shorter wavelengths and vice versa. In simple terms, the higher the frequency, the bluer the light, while lower frequencies manifest as red or longer wavelengths.
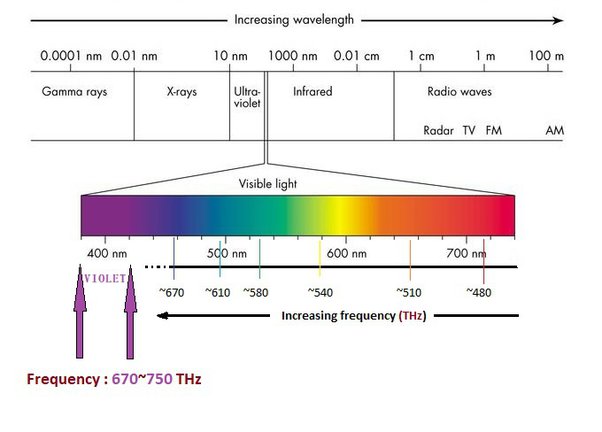
Frequency
2. Reflectivity and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
To understand how materials reflect light, we must consider the interaction between light and the electromagnetic spectrum. When light encounters an object, it can be absorbed, transmitted, or reflected. The reflective properties of a material depend on its atomic and molecular structure, as well as the energy levels of its electrons. Different materials have varying abilities to absorb or reflect certain frequencies of light.
In terms of the electromagnetic spectrum, visible light occupies a specific range of frequencies, spanning from violet (highest frequency) to red (lowest frequency). Materials that can reflect higher frequency light are typically those that exhibit strong reflectivity within the blue and violet regions of the spectrum. However, it's important to note that materials rarely reflect all light within a given frequency range uniformly.
Reflectivity and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
3. High-Frequency Reflective Materials
Several materials are known for their exceptional ability to reflect light with high frequencies. These materials are often utilized in scientific, industrial, and technological applications where reflecting specific frequencies of light is essential. Here are some notable examples:
a. Metals:
Certain metals, such as silver and aluminum, possess excellent reflectivity across a broad range of frequencies, including higher frequency blue and violet light. These metals are commonly used in mirrors, reflective coatings, and optical applications.
b. Dielectric Mirrors:
Dielectric mirrors, composed of alternating layers of dielectric materials, are engineered to maximize reflectivity at specific frequencies. By carefully selecting the thickness and refractive indices of the layers, these mirrors can exhibit high reflectivity for specific wavelengths, including those in the blue and violet regions.
c. Fluorescent Materials:
While not strictly reflecting light, fluorescent materials have the ability to absorb light of one frequency and emit light of a higher frequency. This phenomenon, known as fluorescence, enables certain materials to exhibit strong reflectivity in the higher frequency range of the spectrum.
d. Photonic Crystals:
Photonic crystals are carefully designed materials with a periodic structure that interacts with light in unique ways. These crystals can be engineered to reflect specific frequencies or ranges of frequencies, including higher frequency light.
The question of which material reflects light with the highest frequency unravels the intricate relationship between light, frequency, and reflective properties. While metals like silver and aluminum, dielectric mirrors, fluorescent materials, and photonic crystals exhibit remarkable abilities to reflect high-frequency light, the reflective properties of materials are influenced by complex factors. By comprehending the principles behind light reflection, we gain insights into the fascinating world of high-frequency reflectivity, enabling advancements in various scientific, industrial, and technological domains.