What Determines the Speed at Which Data Travels?
In today's digital era, the speed at which data travels has become crucial for various aspects of our lives, ranging from communication and entertainment to business operations and scientific research. Understanding the factors that determine data transmission speed is essential for optimizing network performance and ensuring efficient data transfer. This article explores the key elements that influence the speed at which data travels, shedding light on the technical aspects behind this critical process.
I. Bandwidth
One of the primary factors that influence data transmission speed is the available bandwidth. Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection in a given time frame. Higher bandwidth allows for faster data transfer, as more information can be sent simultaneously.
The bandwidth of a network connection is determined by the infrastructure in place, such as the type of network technology being used (e.g., Ethernet, fiber optics) and the quality of the network equipment.

Ethernet
II. Latency
Latency, also known as network delay, is another crucial factor impacting data transmission speed. It refers to the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination.
Latency is influenced by various factors, including the distance between the sender and receiver, the number of network devices the data must traverse, and the processing time at each intermediate point. Lower latency results in faster data transmission, particularly for real-time applications like video streaming and online gaming.
III. Network Congestion
Network congestion occurs when the volume of data being transmitted surpasses the capacity of the network infrastructure. This congestion can lead to delays and slower data transfer speeds.
Network congestion
Factors contributing to network congestion include high data demand, insufficient network infrastructure, and suboptimal routing. Network administrators employ various techniques to manage and mitigate congestion, such as traffic shaping, quality of service (QoS) policies, and load balancing.
IV. Signal Interference
The presence of signal interference can significantly impact the speed at which data travels. Interference can arise from various sources, including electromagnetic radiation, physical obstructions, and competing signals.
In wireless networks, interference can cause packet loss, data corruption, and retransmissions, leading to slower data transmission speeds. Implementing robust signal modulation techniques, utilizing higher frequencies, and minimizing sources of interference can help improve data transfer rates.
V. Network Protocol Efficiency
The efficiency of network protocols plays a vital role in determining data transmission speed. Network protocols define the rules and procedures for data exchange between devices. Efficient protocols can optimize data transfer by minimizing overhead, reducing retransmissions, and improving error correction mechanisms.
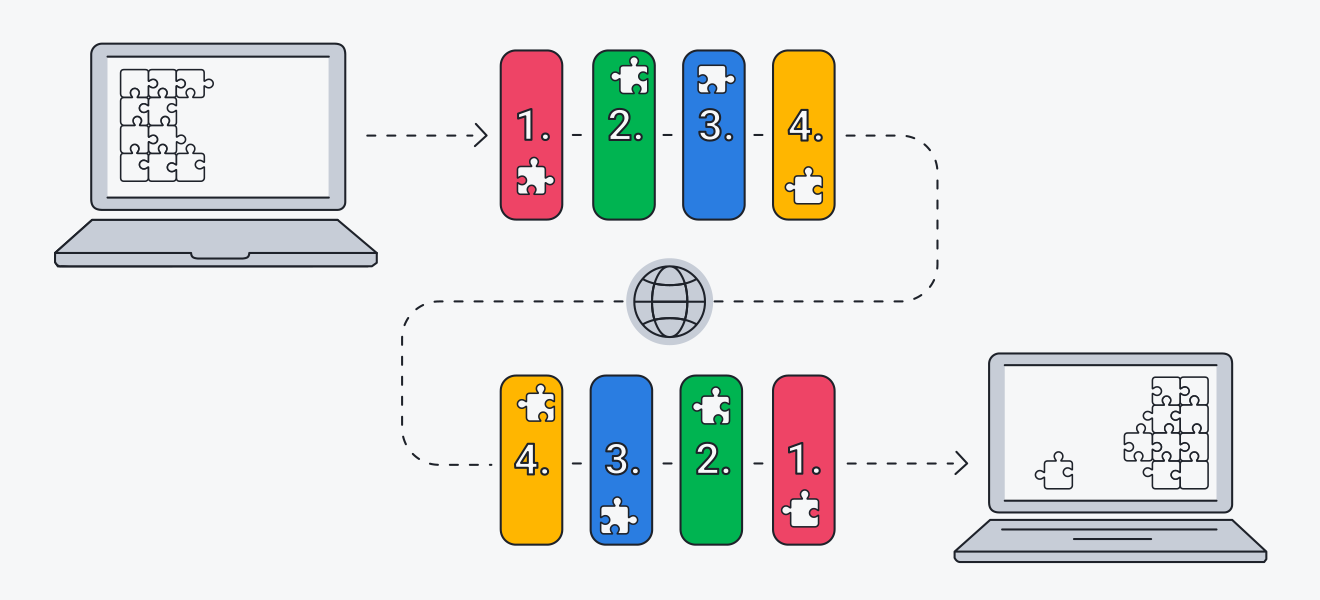
TCP
Popular network protocols such as TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) have different trade-offs between reliability and speed, with TCP offering error checking and congestion control, while UDP prioritizes speed over reliability.
VI. Hardware and Software Configuration
The configuration of both hardware and software components can influence data transmission speed. On the hardware side, factors like the quality and capacity of network adapters, routers, and switches can impact the overall network performance.
Optimizing software settings, including network configurations, operating system parameters, and firewall rules, can also enhance data transfer speeds. Regular maintenance, updates, and hardware upgrades can help ensure optimal performance.
VII. Distance and Routing
The physical distance between the sender and receiver can affect data transmission speed, particularly in wide-area networks (WANs). Data traveling long distances may encounter more network devices and potential bottlenecks, leading to increased latency and slower speeds.
Efficient routing algorithms and infrastructure, such as Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and caching mechanisms, can minimize the impact of distance and optimize data delivery.
VIII. Conclusion
The speed at which data travels is determined by a combination of factors that interact within network infrastructures. Bandwidth availability, latency, network congestion, signal interference, network protocol efficiency, hardware and software configuration, as well as distance and routing, all contribute to the overall data transmission speed.
Understanding and optimizing these elements is essential for ensuring efficient and reliable data transfer in various applications. As technology continues to advance, it becomes increasingly important to focus on improving these factors to meet the growing demands of our interconnected world.