Which Food Temperature Promotes Optimal Bacterial Growth: An In-Depth Analysis
In the realm of food safety, understanding the conditions under which bacteria thrive is of utmost importance. One critical factor that influences bacterial growth is temperature. This article aims to explore the relationship between food temperature and bacterial proliferation, delving into the temperature ranges that allow bacteria to grow optimally. By examining various types of foods and their ideal temperature conditions, we can gain valuable insights into preserving food quality and minimizing health risks associated with bacterial contamination.
1. The Role of Temperature in Bacterial Growth:
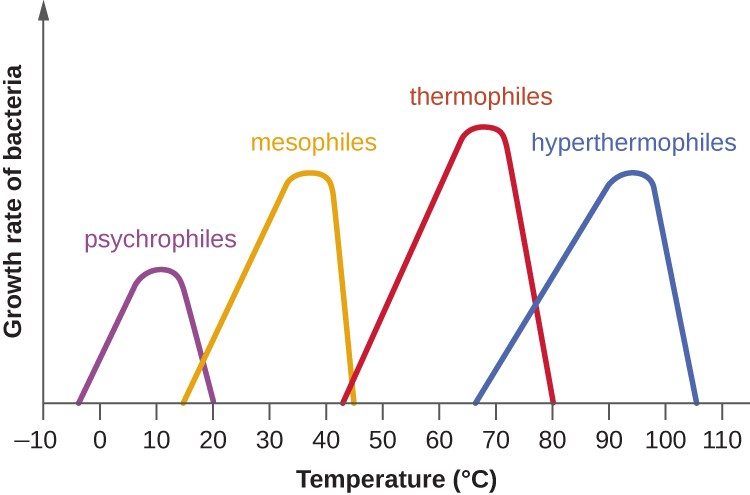
The Role of Temperature in Bacterial Growth
Bacteria are ubiquitous microorganisms that require specific environmental conditions to proliferate. Temperature serves as a crucial factor affecting their growth rate. Understanding the temperature ranges that facilitate bacterial growth is vital for preventing foodborne illnesses.
2. Ideal Temperature for Bacterial Growth:
Ideal Temperature for Bacterial Growth
2.1 Temperature Danger Zone: The temperature danger zone for bacterial growth is typically between 40°F (4°C) and 140°F (60°C). Within this range, bacteria multiply rapidly, posing a significant risk to food safety. It is imperative to minimize the time that food spends in this temperature range to avoid bacterial contamination.
3. Specific Temperature Requirements for Different Food Types:
3.1 High-Risk Foods: High-risk foods, such as meat, poultry, dairy products, and cooked rice, are particularly susceptible to bacterial growth. They require specific temperature control measures to prevent the proliferation of harmful bacteria.
3.2 Meat and Poultry: Meat and poultry should be stored at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) to inhibit bacterial growth. Proper refrigeration slows down the multiplication of bacteria, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
3.3 Dairy Products: Dairy products, including milk, cheese, and yogurt, are highly perishable and prone to bacterial contamination. These items should be stored at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) to maintain freshness and prevent bacterial growth.
3.4 Cooked Rice: Cooked rice is a common breeding ground for bacteria if not handled correctly. It should be kept at temperatures above 140°F (60°C) or promptly refrigerated to inhibit bacterial growth.
4. Safe Food Handling Practices:
4.1 Cooking Temperatures: Proper cooking temperatures are crucial for destroying harmful bacteria. Foods like poultry, ground meat, and seafood should be cooked to an internal temperature of at least 165°F (74°C) to ensure bacteria are eliminated.
4.2 Cooling and Refrigeration: Rapid cooling and refrigeration are essential for preventing bacterial growth in cooked foods. Ensure that perishable items are promptly refrigerated at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) to maintain their safety and quality.
4.3 Food Thermometers: The use of food thermometers is highly recommended to accurately measure the internal temperature of cooked foods. This helps confirm whether the desired temperature for bacteria elimination has been reached.
5. Importance of Proper Food Storage:
5.1 Refrigeration: Refrigeration is a crucial tool for slowing down bacterial growth. By storing perishable foods at temperatures below 40°F (4°C), bacterial multiplication can be significantly inhibited.
5.2 Freezing: Freezing foods at or below 0°F (-18°C) suspends bacterial growth altogether. It is an effective method for long-term storage, ensuring food safety and extending shelf life.
Understanding the relationship between food temperature and bacterial growth is essential for ensuring food safety and preventing foodborne illnesses. By adhering to proper temperature control measures, practicing safe food handling techniques, and implementing adequate storage practices, we can minimize the risk of bacterial contamination and protect public health. Remember, maintaining optimal food temperatures is a key factor in preserving both taste and well-being.