Determining the Optimal Representation of Concentration: Exploring the 1.75 M K2CrO4 Solution
Representing the concentration of a solution accurately is essential for scientific research, experimental procedures, and various applications. When dealing with a 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution, determining the most effective way to express its concentration becomes crucial. In this article, we will delve into the different methods used to represent solution concentration, evaluate their suitability for the given 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution, and discuss the significance of choosing the appropriate representation.
1. Understanding Solution Concentration
Solution concentration refers to the amount of solute (substance being dissolved) in a given quantity of solvent (dissolving medium). It is crucial to express concentration accurately to ensure consistency and precision in scientific studies and practical applications. Common units for expressing concentration include molarity (M), mass/volume percent, and mole fraction.
Understanding Solution Concentration
2. Molarity (M) as a Concentration Unit
Molarity (M) is a widely used unit for representing concentration. It is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. In the case of the 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution, it signifies that there are 1.75 moles of K2CrO4 dissolved in each liter of the solution. Molarity provides a straightforward and commonly accepted method to express concentration, making it suitable for various scientific applications.
3. Suitability of Molarity for the 1.75 M K2CrO4 Solution
Given that the concentration of the K2CrO4 solution is 1.75 M, expressing it using molarity is appropriate. Molarity is well-suited for quantifying the concentration of a solution accurately, and its use in scientific research and experimental procedures allows for easy comparison and reproducibility of results. Therefore, representing the 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution using molarity provides a clear and standardized measurement.
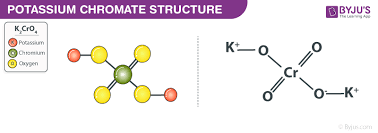
K2CrO4
4. Other Possible Concentration Representations
While molarity is the preferred method for representing the concentration of the 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution, it is worth mentioning other possible representations. These include mass/volume percent and mole fraction. Mass/volume percent expresses the mass of the solute in grams per volume of solution (usually in percent). However, in the case of the 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution, molarity is a more suitable and commonly used unit for concentration representation.
Mole fraction, on the other hand, quantifies the ratio of moles of a specific component to the total moles of all components in a solution. While mole fraction can be useful in certain contexts, it may not be the most practical representation for the 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution, as it does not provide a direct measure of the volume or mass of the solution.
5. Importance of Choosing the Appropriate Representation
Selecting the appropriate representation for solution concentration is crucial for clear communication, accurate measurement, and consistency in scientific research and practical applications. The chosen representation should align with the properties of the solution and the specific requirements of the experiment or analysis. Using the most suitable unit, such as molarity for the 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution, ensures that concentration information is conveyed effectively and facilitates proper comparison and interpretation of results.
Representing the concentration of a solution accurately is essential in scientific research and practical applications. In the case of the 1.75 M K2CrO4 solution, expressing its concentration using molarity provides a clear and widely accepted representation. Molarity quantifies the moles of solute per liter of solution, allowing for easy comparison, reproducibility, and consistent measurement. While other representations such as mass/volume percent and mole fraction are available, molarity is the most suitable and practical unit for the given solution. Choosing the appropriate representation of concentration ensures clear communication, accurate measurement, and reliable data interpretation in scientific endeavors.